Russian Union of Evangelical Christians-Baptists
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Kue busa (schuimpjes) Kue busa (bahasa Belanda: schuimpje, bahasa Inggris: meringue) adalah kue kering yang manis dan ringan. Adonan dibuat dari putih telur yang dikocok hingga berbusa dengan gula halus hingga kaku. Kue dibentuk dengan bantuan kantong segitiga, dan dipanggang perlahan di dalam oven. Kue ini sama sekali tidak memakai tepung terigu, dan mudah larut di dalam mulut. Beberapa resep kue busa memakai bahan pengikat seperti pati jagung (bahan pencampur gula tepung) atau krim tartar. Kue…
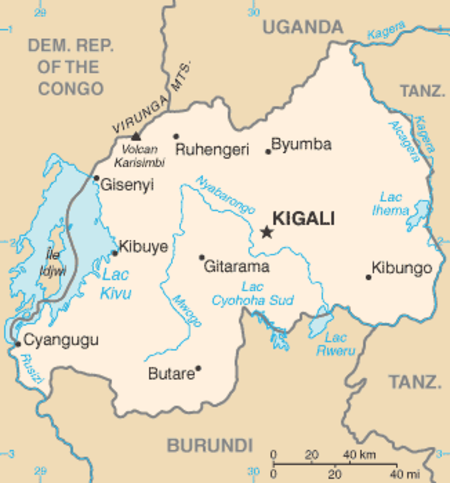
Sungai NyabarongoPertemuan Nyawarungu (kanan atas) dan Ruvuvu (kiri atas) untuk membentuk Sungai Kagera (depan).Peta Rwanda, menunjukkan lokasi Sungai Nyabarongo, yang mengalir pertama ke utara, kemudian tenggara melewati Kigali, lalu ke timur di sepanjang perbatasan tenggara RwandaLokasiNegaraRwanda, Burundi, TanzaniaCiri-ciri fisikHulu sungai - koordinat2°12′13″S 29°34′04″E / 2.203503°S 29.567728°E / -2.203503; 29.567728 - elevasi1.…

German operatic tenor (born 1970) Klaus Florian VogtVogt in 2015Born12 April 1970Heide, Schleswig-Holstein, West GermanyEducationLübeck Academy of MusicOccupationClassical operatic tenorOrganizationSemperoper Klaus Florian Vogt (born 12 April 1970) is a German operatic tenor. He has often sung roles written by Richard Wagner. Career Klaus Florian Vogt was a hornist first and played for several years with the Hamburg Philharmonic. He studied voice at the Lübeck Academy of Music and was first en…

Daha SelatanKecamatanKantor kecamatan Daha SelatanPeta lokasi Kecamatan Daha SelatanNegara IndonesiaProvinsiKalimantan SelatanKabupatenHulu Sungai SelatanPemerintahan • CamatNafarin, SSTP, M.SiPopulasi • Total39,236 jiwaKode Kemendagri63.06.07 Kode BPS6306090 Luas322,82 km²Desa/kelurahan16/- Daha Selatan adalah kecamatan di Kabupaten Hulu Sungai Selatan, Kalimantan Selatan, Indonesia. Penduduknya menganut agama Islam dan sebagian 90% suku Banjar, serta 10% suku Nusa…

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2018年3月17日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:羅生門 (電影) — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源(判定指引)。 此�…

Type of soil EntisolEntisol profile showing little or no evidence of pedogenic horizon developmentUsed inUSDA soil taxonomy Entisols are soils, as defined under USDA soil taxonomy, that do not show any profile development other than an A-horizon (or “A” horizon). Entisols have no diagnostic horizons, and are unaltered from their parent material, which could be unconsolidated sediment, or rock. Entisols are the most common soils, occupying about 16% of the global ice-free land area. Because o…

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Christian Paul et Paul. Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article ne s'appuie pas, ou pas assez, sur des sources secondaires ou tertiaires (janvier 2023). Pour améliorer la vérifiabilité de l'article ainsi que son intérêt encyclopédique, il est nécessaire, quand des sources primaires sont citées, de les associer à des analyses faites par des sources secondaires. Christian Paul Christian Paul à Lormes l…

Mount TahanGunung Tahanڬونوڠ تاهنTitik tertinggiKetinggian2.187 m (7.175 ft)[1]Puncak2.140 m (7.020 ft)[1]Masuk dalam daftarUltraRibuKoordinat4°37′57″N 102°14′03″E / 4.63250°N 102.23417°E / 4.63250; 102.23417Koordinat: 4°37′57″N 102°14′03″E / 4.63250°N 102.23417°E / 4.63250; 102.23417 [1]GeografiMount TahanMalaysiaLetakTaman Negara National Park, Pahang, MalaysiaPegu…

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Птиц�…

Swedish multinational manufacturing company This article is about the Volvo Group (AB Volvo). For the separate manufacturer of passenger automobiles, see Volvo Cars. For other uses, see Volvo (disambiguation). AB VolvoCompany typeAktiebolagTraded asNasdaq Stockholm: VOLV A, Nasdaq Stockholm: VOLV BISINSE0000115446IndustryAutomotiveFounded1927; 97 years ago (1927)FoundersAssar Gabrielsson and Gustav LarsonHeadquartersGothenburg, SwedenArea servedWorldwideKey peopleCarl…

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Missouri Circuit Courts – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Jackson County courthouse for the 16th Circuit Court in Kansas City The Missouri Circuit Courts are the state trial courts of original jur…

State park in Bucks County, Pennsylvania Ralph Stover State ParkIUCN category III (natural monument or feature)The view of Tohickon Creek from the top of High Rocks during autumn.Location of Ralph Stover State Park in PennsylvaniaShow map of PennsylvaniaRalph Stover State Park (the United States)Show map of the United StatesLocationBucks, Pennsylvania, United StatesCoordinates40°26′04″N 75°05′55″W / 40.43444°N 75.09861°W / 40.43444; -75.09861Area45 acres (18&#…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Desember 2022. Galangan kapal Buenos Aires pada tahun 1915. Sejarah ekonomi Argentina merupakan salah satu yang paling dikaji oleh para ekonom akibat Paradoks Argentina: Argentina pernah menjadi negara yang tergolong maju pada awal abad ke-20, tetapi kemudian mengalami…

Sepasang sepatu roda Sepatu roda adalah sepatu atau pengikat yang dipasang pada sepatu yang dipakai agar pemakainya dapat berguling-guling di atas roda. Sepatu roda pertama adalah desain seluncur roda , yang secara efektif merupakan sepatu selajur dengan roda yang menggantikan bilahnya. Belakangan gaya sepatu caturroda menjadi lebih populer, terdiri dari empat roda yang disusun dalam konfigurasi yang sama seperti mobil pada umumnya. Bersepatu roda adalah suatu hobi, olah raga, dan moda transport…

此条目页的主題是香港九龍的渡船街。关于其他地方的同名街道,請見「渡船街」。 Ferry Street渡船街渡船街與西九龍走廊的交匯路段,此段連同渡船街天橋隸屬於5號幹線。命名緣由命名文件:1941年10月24日憲報第1260號政府公告、1947年5月23日憲報第431號政府公告、1975年3月14日憲報第585號政府公告、2020年10月16日憲報第5984號政府公告命名日期1941年10月24日[1]道路長…

星洲网网站类型新闻网站语言简体中文總部 马来西亚雪兰莪州八打灵再也Semangat路19号(星洲日报总部)持有者世华多媒体有限公司編輯卜亚烈网址www.sinchew.com.my商业性质是注册选择性(个人新闻空间)推出时间2000年4月21日,24年前(2000-04-21)內容許可保有版权 星洲网,是一家马来西亚线上免费综合新闻网站,也是马来西亚销售量最高的中文报《星洲日报》的�…

此條目可能包含不适用或被曲解的引用资料,部分内容的准确性无法被证實。 (2023年1月5日)请协助校核其中的错误以改善这篇条目。详情请参见条目的讨论页。 各国相关 主題列表 索引 国内生产总值 石油储量 国防预算 武装部队(军事) 官方语言 人口統計 人口密度 生育率 出生率 死亡率 自杀率 谋杀率 失业率 储蓄率 识字率 出口额 进口额 煤产量 发电量 监禁率 死刑 国债 外…
Carte thermiqueReprésentation graphique des données statistiques sur les mouvement d'yeux (eye-tracking) sur une page d'accueil de Wikipedia : plus c'est rouge, plus les yeux des internautes se posent sur cette région.Type Type de carte géographique (d), carte géographique, représentation graphique de données statistiques (en)modifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata Une carte thermique (carte de fréquentation, ou heat map en anglais signifiant littéralement carte de chaleur[…

Siciliano occidentaleParlato in Italia Parlato in Sicilia TassonomiaFilogenesiLingue indoeuropee Italiche Romanze Italo-occidentali Italo-dalmate Siciliano Siciliano occidentale Codici di classificazioneLinguist Listscn-wes (EN) Glottologwest2346 (EN) Mappa dei dialetti siciliani: il siciliano occidentale è indicato con la lettera a Manuale Il dialetto siciliano occidenta…

User interface element The splash screen for version 2.65 of Blender A splash screen is a graphical control element consisting of a window containing an image, a logo, and the current version of the software. A splash screen can appear while a game or program is launching. A splash page is an introduction page on a website.[1][2] A splash screen may cover the entire screen or web page; or may simply be a rectangle near the center of the screen or page. The splash screens of opera…

