Castellan
|
Read other articles:

Unità militari Unità Numero di soldati Grado del comandante Gruppo di fuoco 2-5 Caporale SquadraCarroPezzo 10-151 carro1 pezzo Caporal maggiore,Sergente PlotonePlotone carriSezione 30-504 carri2 o più pezzi Maresciallo,Sottotenente,Tenente CompagniaSquadroneBatteria 100-25010-20 carrivariabile Tenente,Capitano BattaglioneGruppo 500-1.000 Maggiore,Tenente colonnello, Reggimento 1.500-3.000 Colonnello Brigata 4.000-6.000 Generale di brigata Divisione 10.00030.000 Generale di divisione Corpo d'a…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada April 2016. Comboios de PortugalIndustriTransportasi relDidirikan1951KantorpusatLisbon, PortugalTokohkunciManuel Queiró,Vicente Pereira,Isabel VicenteProdukTransportasi rel, KargoPendapatan € -225.6 juta (2013)[1]Laba operasi € -75.35 juta (2013)[1]…

Ассирийская цилиндрическая печать из известняка и современный гипсовый слепок её изображения, содержащего мотив поклонения богу Шамашу; Лувр Цилиндрическая печать — выточенный из камня небольшой цилиндр с продольным осевым отверстием, который использовался в Древн�…

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. K. Буквы со сходным начертанием: Κ · κ · К · к · ĸ Буква латиницы K Kk Изображение ◄ G H I J K L M N O ► ◄ g h i j k l m n o ► Характеристики Название K: latin capital letter kk: latin small letter k Юникод K: U+004Bk: …

Glorified visual presentation Not to be confused with Food and sexuality. Tacos A jelly roll Food porn (or foodporn) is a glamourized visual presentation of cooking or eating in advertisements, infomercials, blogs, cooking shows, and other visual media.[1] Its origins come from a restaurant review e-commerce platform called Foodporn.[2] Food porn often takes the form of food photography with styling that presents food provocatively, in a similar way to glamour photography or porn…

Genetic neurodegenerative disease with brain iron accumulation Medical conditionPantothenate kinase-associated neurodegenerationOther namesNeurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation 1PantetheineSpecialtyNeurologySymptomsDystonia, parkinsonism, dementiaUsual onsetUnder 10 years (classical), Over 10 years (atypical)TypesClassical, atypicalCausesPANK2 mutationFrequency1–3 per 1 million people Pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration (PKAN), formerly called Hallervorden–Spatz syndrom…

Village in Michigan, United StatesKalkaska, MichiganVillageVillage of KalkaskaDowntown Kalkaska along Cedar StreetNickname: Trout Capital of MichiganMotto: Space to GrowLocation within Kalkaska CountyKalkaskaLocation within the state of MichiganCoordinates: 44°44′04″N 85°10′48″W / 44.73444°N 85.18000°W / 44.73444; -85.18000Country United StatesState MichiganCountyKalkaskaTownshipKalkaskaPlatted1873Incorporated1887Founded byAlbert A. AbbottG…

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Bendigo Advertiser – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Australian regional newspaper Bendigo AdvertiserFront page of the Bendigo Advertiseron 3 April 2010FormatTabloidOwner(s)Australian Co…

iPhone 5PembuatApple Inc.SeriiPhoneJaringanGSM, CDMA, 3G, 4G LTEKetersediaan menurut negara 21 September 2012 Amerika SerikatKanadaBritania RayaPrancisJermanAustraliaJepangHong KongSingapura Dihentikan10 September 2013 (2013-09-10)PendahuluiPhone 4SPenerusiPhone 5C Dan iPhone 5STerkaitiPod Touch generasi ke-5TipeTelepon cerdasFaktor bentukBatangDimensi1.238 mm (48,7 in) H586 mm (23,1 in) W76 mm (3,0 in) DBerat112 g (3,95 oz)Sistem OperasiiOS 6.0CPU1&#…

Telephone area codes for Broward County, Florida This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Area codes 954 and 754 – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Area codes 954 and 754 are the telephone area codes in the North American Numberi…

20th-century Indian independence activist and socialist political leader Ram Manohar LohiaLohia on a 1977 stamp of IndiaBorn(1910-03-23)23 March 1910Akbarpur, United Provinces of Agra and Oudh, British IndiaDied12 October 1967(1967-10-12) (aged 57)New Delhi, IndiaAlma materUniversity of Calcutta (BA)Humboldt University of Berlin (PhD)Political partyIndian National CongressPraja Socialist PartySamyukta Socialist PartyMovementQuit India MovementIndian independence movementWebsitewww.lohi…

Corpus of historical carved writings of Khmer origin Khmer inscriptions are a corpus of post-5th century historical texts engraved on materials such as stone and metal ware found in a wide range of mainland Southeast Asia (Cambodia, Vietnam, Thailand and Laos) and relating to the Khmer civilization. The study of Khmer inscriptions is known as Khmer epigraphy. Khmer inscriptions are the only local written sources for the study of ancient Khmer civilization.[1] More than 1,200 Khmer inscri…

French light twin piston-engine transport, 1947 Corse SO 93 Role Mail/passenger transportType of aircraft National origin France Manufacturer SNCASO First flight 17 July 1947 Primary user Aeronavale Number built 64 The Sud-Ouest Corse was a French mail and passenger transport aircraft, built by SNCASO.[1] Development and design The Corse began as the S.O.90 Cassiopée, a nine-passenger aircraft. The S.O.93 Corse and S.O.94 Corse II prototypes were developed as the S.O.95 Corse III. …
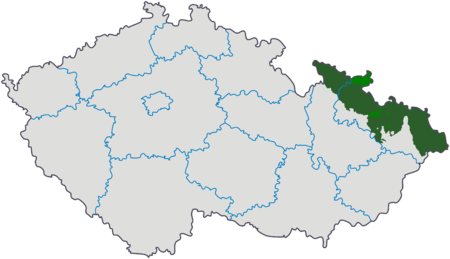
Slesia cecaČeské Slezsko Hradec nad Moravicí Stati Rep. Ceca Regioni Slesia CapoluogoOstrava Superficie4 459 km² Abitanti1 000 000 Linguececo, slesiano Il territorio della Slesia ceca. La Slesia ceca (in ceco České Slezsko; in slesiano Czeski Ślůnsk; in tedesco Tschechisch-Schlesien; in polacco Śląsk Czeski), una delle tre regioni ceche, è la parte della Slesia all'interno dei confini cechi. È situata nel nord-est della Repubblica Cec…

Artikel ini membutuhkan rujukan tambahan agar kualitasnya dapat dipastikan. Mohon bantu kami mengembangkan artikel ini dengan cara menambahkan rujukan ke sumber tepercaya. Pernyataan tak bersumber bisa saja dipertentangkan dan dihapus.Cari sumber: Minggu Sengsara – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTORUntuk upacara kebaktian di gereja dalam minggu yang sama, lihat Pekan Suci. Peristiwa-peristiwa dalamKehidupan Yesusmenurut Injil Masa kanak-kan…

Tigri per la liberazione della patria TamilBandiera delle Tigri TamilAttivamaggio 1976 - maggio 2009 Nazione Sri Lanka ContestoSri Lanka settentrionale IdeologiaNazionalismo TamilSocialismo rivoluzionario ComponentiFondatoriVelupillai Prabhakaran AttivitàAzioni principaliGuerra civile in Sri LankaAttacco di ThirunelveliMassacro di Aranthalawa Le Tigri per la liberazione della patria Tamil (Tamil: தமிழீழ விடுதலைப் புலிகள், ISO 15919: tamiḻ…

South Indian dynasty This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (January 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Eastern ChalukyasChalukyas of Vengi624–1189 Eastern Chalukya coin. Central punchmark depicting a Boar standing left. Incuse of punchmarks. Map of India c. 753 CE. The Eastern Chalukya kingdom is shown on the eastern coast.Capital…
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会波兰代表團波兰国旗IOC編碼POLNOC波蘭奧林匹克委員會網站olimpijski.pl(英文)(波兰文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員206參賽項目24个大项旗手开幕式:帕维尔·科热尼奥夫斯基(游泳)和马娅·沃什乔夫斯卡(自行车)[1]闭幕式:卡罗利娜·纳亚(皮划艇)[2…

莎拉·阿什頓-西里洛2023年8月,阿什頓-西里洛穿著軍服出生 (1977-07-09) 1977年7月9日(46歲) 美國佛羅里達州国籍 美國别名莎拉·阿什頓(Sarah Ashton)莎拉·西里洛(Sarah Cirillo)金髮女郎(Blonde)职业記者、活動家、政治活動家和候選人、軍醫活跃时期2020年—雇主內華達州共和黨候選人(2020年)《Political.tips》(2020年—)《LGBTQ國度》(2022年3月—2022年10月)烏克蘭媒體�…

Cabinet of Bangladesh (2024-) This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: Fifth Hasina ministry – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2024) Fifth Hasina Ministry21st Cabinet of BangladeshSheikh Hasina Wazed Hon'ble Prime Minister of BangladeshDate formed11 January 2024&#…



