Dayr al-Shaykh
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Arondisemen ke-5 Paris 5e arrondissement de ParisArondisemen kotaPemandangan Rue Soufflot dengan Panthéon sebagai latar belakangnya Lambang kebesaranLokasi di wilayah ParisKoordinat: 48°50′50″N 2°20′40″E / 48.84722°N 2.34444°E / 48.84722; 2.34444Koordinat: 48°50′50″N 2°20′40″E / 48.84722°N 2.34444°E / 48.84722; 2.34444NegaraPrancisRegionÎle-de-FranceDepartemenParisKomuneParisPemerintahan • Walikota (2020–…

Hooters, Inc.JenisSwastaIndustriLayanan makananDidirikan1 April 1983; 40 tahun lalu (1983-04-01)Clearwater, Florida, Amerika SerikatPendiriLynn D. StewartGil DiGiannantonioEd DrosteBilly RanieriKen WimmerDennis JohnsonKantorpusatAtlanta, Georgia, A.S.Cabang430+[1]Wilayah operasiSeluruh duniaProdukBurger, sayap ayam, makanan laut dan barSitus webwww.hooters.com Hooters, Inc., adalah nama dagang dari dua jaringan restoran Amerika Serikat yang dimiliki secara pribadi: Hooters of Americ…

Basilika Bunda Maria dari PiatBasilika Minor Bunda Maria dari Piat di CagayanPiat BasilicaBasílica Menor de Nuestra Señora de Piatcode: es is deprecated (Spanyol)Basilika Bunda Maria dari PiatBasilika Bunda Maria dari PiatTampilkan peta LuzonBasilika Bunda Maria dari PiatTampilkan peta Filipina17°47′13″N 121°28′48″E / 17.78698°N 121.48013°E / 17.78698; 121.48013Koordinat: 17°47′13″N 121°28′48″E / 17.78698°N 121.48013°E…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada November 2022. Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Oktober 2022. Du boudoi…

Gandhi memimpin Satyagraha Satyagraha adalah sebutan untuk gerakan perlawanan rakyat sipil untuk memprotes monopoli garam yang diberlakukan oleh pemerintahan Inggris di India.[1] Gerakan Satyagraha dipimpin oleh Mahatma Gandhi dengan alasan bahwa garam merupakan kebutuhan vital bangsa India.[1] Aturan monopoli garam yang ditetapkan Inggris berisi larangan untuk mengumpulkan atau menjual garam dan paksaan untuk membeli garam kepada Inggris dengan pajak yang tinggi.[1] 12 M…
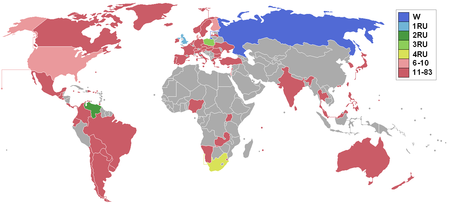
Beauty pageant edition Miss World 1992Miss World 1992 TitlecardDate12 December 1992PresentersBilly Dee WilliamsJerry HallDoreen MorrisSuanne BraunDeborah SheltonVenueSun City Entertainment Center, Sun City, South AfricaBroadcasterE!SABCEntrants83Placements10DebutsCroatiaRussiaSloveniaUkraineWithdrawalsBelizeGhanaHondurasKenyaPeruYugoslaviaReturnsBermudaCanadaHong KongSeychellesSri LankaUgandaZambiaWinnerJulia Kourotchkina RussiaPersonalityAna María Johanis Iglesias GuatemalaBest Nati…

Peta yang menunjukkan letak San Jose del Monte. Data sensus penduduk diSan Jose del Monte City Tahun Populasi Persentase 1995201.394—2000315.80710.14%2007439.0904.65% San Jose del Monte City adalah kota di provinsi Bulacan, Filipina. Pada tahun 2007, munisipalitas ini memiliki populasi sebesar 439.090 jiwa. Pembagian wilayah Secara politis San Jose del Monte terbagi atas 59 barangay, yaitu: No. Barangay Captain SK Chairman (per 25 Oktober 2010) Distrik Kode pos Populasi01 Mei 2000 Populasi01 A…

Irish association football club This article is about the current League of Ireland club. For the earlier League of Ireland club, see Cork City F.C. (1938–1940). For the women's football club, see Cork City W.F.C. Football clubCork CityFull nameCork City Football ClubNickname(s)Rebel Army, CityFounded1984; 40 years ago (1984)GroundTurners CrossCapacity7,485OwnerDermot Usher[1]ChairmanDeclan Carey[2]ManagerTim Clancy[3]LeagueLeague of Ireland First Divi…

العلاقات الإكوادورية البولندية الإكوادور بولندا الإكوادور بولندا تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الإكوادورية البولندية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين الإكوادور وبولندا.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: �…

Estonian football club This article needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (June 2019) Football clubSillamäe KalevFull nameJalgpalliklubi Sillamäe KalevFounded1957; 67 years ago (1957)GroundSillamäe Kalev StadiumCapacity800[1]ChairmanAleksandr StarodubtsevManagerVadym DobizhaLeagueII liiga (north/east)2022II liiga, 10thWebsiteClub website Home colours Away colours JK Sillamäe Kalev, commonly know…

Defunct flying squadron of the Royal Air Force No. 140 Squadron RAFActive1918-19181941-1945Country United KingdomBranch Royal Air ForceRolePhoto ReconnaissanceMotto(s)Foresight[1]Military unit No. 140 Squadron of the Royal Air Force was a Second World War photo-reconnaissance squadron that operated between 1941 and 1945.[2] History Briefly formed during the First World War on 1 May 1918 at RAF Biggin Hill as a home defence squadron with Bristol F.2B Fighters, although b…

العلاقات السودانية الإسواتينية السودان إسواتيني السودان إسواتيني تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات السودانية الإسواتينية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين السودان وإسواتيني.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: �…

DFB Pokal 1997-1998 Competizione Coppa di Germania Sport Calcio Edizione 55ª Luogo Germania Risultati Vincitore Bayern Monaco(9º titolo) Secondo Duisburg Cronologia della competizione 1996-1997 1998-1999 Manuale La DFB-Pokal 1997-1998 è stata la 55ª edizione della Coppa di Germania, 64 squadre si son sfidate a partire dal 14 agosto 1997 fino alla finale giocata il 16 maggio 1998. In finale il Bayern Monaco ha sconfitto il Duisburg 2-1. Indice 1 Primo turno 2 Secondo turno 3 Ottavi di f…

Pour l’article ayant un titre homophone, voir Poésy. Manuscrit du poème Les Assis d’Arthur Rimbaud recopié par Paul Verlaine. La poésie est un genre littéraire très ancien, aux formes variées, écrites généralement en vers mais qui admettent aussi la prose, et qui privilégient l'expressivité de la forme, les mots disant plus qu'eux-mêmes par leur choix (sens et sonorités) et leur agencement (rythmes, métrique, figures de style). Sa définition se révèle difficile et varie sel…

追晉陸軍二級上將趙家驤將軍个人资料出生1910年 大清河南省衛輝府汲縣逝世1958年8月23日(1958歲—08—23)(47—48歲) † 中華民國福建省金門縣国籍 中華民國政党 中國國民黨获奖 青天白日勳章(追贈)军事背景效忠 中華民國服役 國民革命軍 中華民國陸軍服役时间1924年-1958年军衔 二級上將 (追晉)部队四十七師指挥東北剿匪總司令部參謀長陸軍總�…

Public housing estate in Tuen Mun, Hong Kong Sam Shing EstateSam Shing EstateGeneral informationLocation6 Sam Shing Street, Tuen MunNew Territories, Hong KongCoordinates22°22′52″N 113°58′42″E / 22.381174°N 113.978200°E / 22.381174; 113.978200StatusCompletedCategoryPublic rental housingPopulation5,044[1] (2016)No. of blocks3[2]No. of units1,834[2]ConstructionConstructed1980; 44 years ago (1980)AuthorityHong Kong Ho…

MyPaCalcio Segni distintivi Uniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Colori sociali Bianco, rosso Dati societari Città Anjalankoski (Kouvola) Nazione Finlandia Confederazione UEFA Federazione SPL/FBF Campionato Kakkonen Fondazione 1947 Scioglimento2015Rifondazione2018 Stadio Saviniemi(4 067 posti) Sito web www.mypa.fi Palmarès Titoli nazionali 1 Veikkausliiga Trofei nazionali 3 Suomen Cup Dati aggiornati al 5 aprile 2019Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Il Myllykosken Pallo -47, abb…
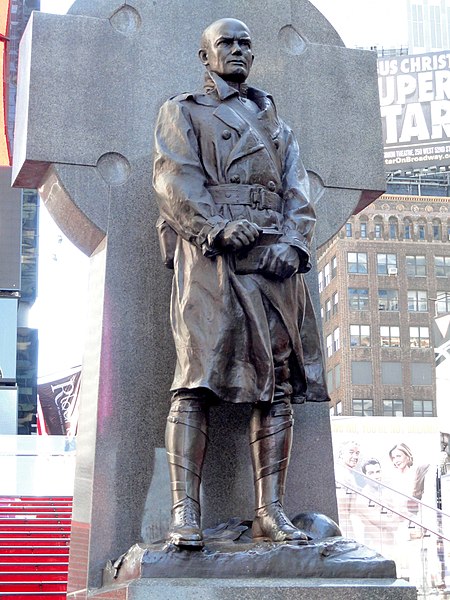

Statue in Times Square, Manhattan, New York, U.S. Father Francis P. DuffyThe sculpture in 2012ArtistCharles KeckYear1936–1937 (1936–1937)TypeSculptureLocationNew York City, New YorkCoordinates40°45′33″N 73°59′06″W / 40.759045°N 73.984987°W / 40.759045; -73.984987 An outdoor 1936–1937 statue of Francis P. Duffy by Charles Keck is installed at Duffy Square, part of Times Square, in the New York City borough of Manhattan.[1] The statue, which w…

Adolf ButenandtBiographieNaissance 24 mars 1903BremerhavenDécès 18 janvier 1995 (à 91 ans)MunichSépulture Waldfriedhof de MunichNom dans la langue maternelle Adolf Friedrich Johann ButenandtNationalité allemandeFormation Université de MarbourgUniversité de GöttingenActivités Biochimiste, homme politique, chimiste, professeur d'universitéConjoint Erika Butenandt (d)Autres informationsA travaillé pour Université Eberhard Karl de TübingenUniversité de GöttingenÉcole polytechniq…

Pour l’article homonyme, voir Lombez (homonymie). Cet article est une ébauche concernant les Pyrénées. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Ambroise de LombezBiographieNaissance 20 mars 1708Décès 25 octobre 1778 (à 70 ans)Activités Prêtre catholique, moineAutres informationsOrdre religieux Ordre des Frères mineursmodifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata Jean de La Peyrie, plus connu…










![The old railway station of Dayr al-Shaykh, on the Jaffa–Jerusalem railway line, situated 0.5 km east of the village site.[3]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7a/BarGioraRailwayStation1.jpg/120px-BarGioraRailwayStation1.jpg)
