Immigration Act of 1891
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Kontributor utama artikel ini tampaknya memiliki hubungan dekat dengan subjek. Artikel ini mungkin memerlukan perapian untuk mematuhi kebijakan konten Wikipedia, terutama dalam hal sudut pandang netral. Silakan dibahas lebih lanjut di halaman pembicaraan artikel ini. (Oktober 2023) (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) UkiramaLogo UkiramaIndustriEnterprise resource planningTentang PerusahaanSitus Webhttps://ukirama.com/PendiriKevin Eka Putra Ignatius Monthy Wangsaha…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada September 2016. Nicholas Reese Art Nicholas Reese Art (lahir 13 Januari 1999) merupakan aktor dari Amerika Serikat. Dia mulai dikenal setelah berperan sebagai Zach Spaulding di drama Guiding Light, dan dia juga pernah muncul di beberapa iklan, program TV dan film seper…

Philippine Army Air Corps (PAAC) (also as PAAC Infantry Battalion, 1942)Pulutong Himpapawid ng Hukbong Katihan ng PilipinasPhilippine Army Air Corps Emblem 1941–42Active1936 – after May 1942 May 1945 – 1 July 1947Country Commonwealth of the PhilippinesBranchPhilippine ArmyTypeCombat Flying Units; Infantry (after c.31 Dec 41)SizeAir Group; Infantry BattalionPart ofFar East Air ForceEngagementsWorld War II Battle of Bataan Philippines campaign (1941–1942) Philippines Campaign (19…

For the field of study, see Neural development. Academic journalDevelopmental NeurobiologyDisciplineNeural developmentLanguageEnglishEdited byBin Chen, Song-Hai Shi, Andreas ProkopPublication detailsFormer name(s)Journal of NeurobiologyHistory1969-presentPublisherWiley-BlackwellFrequencyMonthlyOpen accessDelayed, after 12 monthsImpact factor3.935 (2019)Standard abbreviationsISO 4 (alt) · Bluebook (alt1 · alt2)NLM (alt) · MathSciNet (alt )ISO 4Dev. N…

Bacarai KasihStiker label singel Bacarai KasihSingel oleh Orkes GumarangSisi-AIyo-IyoFormatpelat 10GenreJazz latinmusik MinangDurasi2:48[1]LabelMutiara MA-09-APPenciptaAsbon Madjid Bacarai Kasiah adalah sebuah lagu yang diciptakan oleh Asbon Madjid, serta dinyanyikan oleh Orkes Gumarang dengan iringan vokal oleh Nurseha. Referensi ^ Ijo-Ijo / Batjarai Kasiah. Orkes Gumarang. Mutiara. Pranala luar Ijo-Ijo / Batjarai Kasiah di Discogs (Indonesia) Ijo-Ijo / Batjarai Kasiah di Irama Nu…

Ottignies-Louvain-la-Neuve L'hôtel de ville (1881) à Ottignies. Héraldique Drapeau Administration Pays Belgique Région Région wallonne Communauté Communauté française Province Province du Brabant wallon Arrondissement Nivelles Bourgmestre Julie Chantry (Ecolo) Majorité Ecolo-Avenir-PS SiègesEcoloOLLN 2.0AvenirPSKAYOUX 31109732 Section Code postal OttigniesCéroux-MoustyLimeletteLouvain-la-Neuve 1340134113421348 Code INS 25121 Zone téléphonique 010 Démographie Genti…

This article does not cite any sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: List of extreme points of Brazil – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) The extreme north, south, east and west points of mainland Brazil This is a list of the extreme points of Brazil. Latitude and longitude T…

Sculpture gallery in the Bronx, New York United States historic placeHall of Fame ComplexU.S. National Register of Historic PlacesNew York City Landmark No. 0113 View of the Hall of Fame for Great AmericansLocationBronx Community College campus, The Bronx, New YorkCoordinates40°51′31.7″N 73°54′50.9″W / 40.858806°N 73.914139°W / 40.858806; -73.914139Area2 acres (0.81 ha)Built1901ArchitectStanford WhiteArchitectural styleClassical Revival, Be…

Ilustrasi sosok Amabie yang bersumber pada salah satu surat kabar (kawaraban) dari zaman Edo Amabie (アマビエ) adalah makhluk legenda dalam cerita rakyat Jepang berwujud putri duyung dengan mulut seperti paruh burung yang muncul dari laut. Ia bergerak menggunakan ketiga kaki atau siripnya dan diyakini dapat meramalkan panen berlimpah atau wabah. Amabie kemungkinan merupakan bentuk lain dari Amabiko atau Amahiko, atau dikenal juga sebagai Amahiko-nyūdo (尼彦入道). Sumber tertulis yang me…

Questa voce o sezione deve essere rivista e aggiornata appena possibile. Sembra infatti che questa voce contenga informazioni superate e/o obsolete. Se puoi, contribuisci ad aggiornarla. La Bola de Prata nelle mani di Michel Laurence, uno dei creatori del trofeo La Bola de Prata (in italiano Pallone d'Argento) è un premio annuale assegnato dal 1970 ai migliori undici giocatori del campionato brasiliano di calcio. Il premio è stato istituito dalla rivista brasiliana Placar partendo da un'idea d…
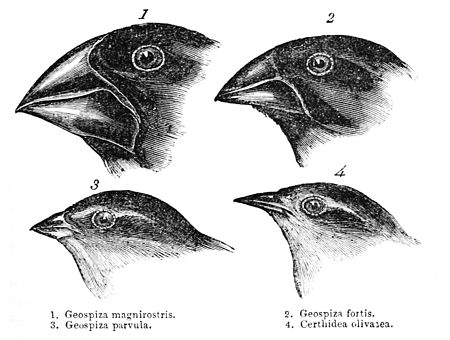
Changes in evolutionary philosophies Part of a series onEvolutionary biologyDarwin's finches by John Gould Index Introduction Main Outline Glossary Evidence History Processes and outcomes Population genetics Variation Diversity Mutation Natural selection Adaptation Polymorphism Genetic drift Gene flow Speciation Adaptive radiation Co-operation Coevolution Coextinction Divergence Convergence Parallel evolution Extinction Natural history Origin of life Common descent History of life Timeline of ev…

Causeway Bay Gedung kepadatan tinggi di Causeway Bay Hanzi tradisional: 銅鑼灣 Hanzi sederhana: 铜锣湾 Makna harfiah: Copper Gong Bay Alih aksara Mandarin - Hanyu Pinyin: Tóngluó wān Yue (Kantonis) - Romanisasi Yale: Tùhnglòh wàahn - Jyutping: Tung4lo4 waan4 Causeway Bay (Hanzi: 銅鑼灣) adalah sebuah kawasan perkotaan di Hong Kong, yang terletak di Pulau Hong Kong, yang mencakup bagian Distrik Wan Chai. Nama Kanton tersebut dapat diromanisasi sebagai Tung Lo Wan seperti Tung L…

1968 novel by Arthur Hailey Airport First Edition (US)AuthorArthur HaileyCountryUnited StatesLanguageEnglishPublisherDoubleday (US)Michael Joseph (UK)Publication date1968Pages440Preceded byHotel Followed byWheels Airport is a bestselling novel by British-Canadian writer Arthur Hailey. Published by Doubleday in 1968, the story concerns a large metropolitan airport and its operations during a severe winter storm. Plot The story takes place at Lincoln International, a fictional…

Это заготовка статьи о гербе. Помогите Википедии, дополнив её. Герб Таиланда Детали Утверждён 18 января 2007 Медиафайлы на Викискладе Герб Таиланда (тайск. ตราแผ่นดินของไทย) — один из государственных символов Таиланда, наряду с флагом и гимном. Герб представ�…

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Западный округ. Западный внутригородской округ город Краснодар Дата основания 1936 год Дата упразднения 1994 Прежние имена Кагановичский, Ленинский районы Микрорайоны Дубинка, Черёмушки, Покровка Площадь 22[1] км² Насел�…

Wickes-class destroyer For other ships with the same name, see USS Foote. History United States NameFoote NamesakeAndrew Hull Foote BuilderFore River Shipbuilding Company, Quincy, Massachusetts Laid down7 August 1918 Launched14 December 1918 Commissioned21 March 1919 Decommissioned6 July 1922 Recommissioned2 July 1940 Decommissioned23 September 1940 Stricken8 January 1941 FateTransferred to United Kingdom, 23 September 1940 United Kingdom NameHMS Roxborough Commissioned23 September 194…

Renault 12InformasiProdusenRenaultMasa produksi1969-1980Bodi & rangkaBentuk kerangka4 pintu sedan 5 pintu station wagonKronologiPendahuluRenault 8 dan 10PenerusRenault 18 Renault 12 merupakan kendaraan sedan dan Station wagon yang diproduksi oleh perusahaan Prancis, Renault sejak tahun 1969 hingga 1980 untuk pasaran Eropa. Mobil ini dirakit di Billancourt, Prancis. Renault 12 dijual di Indonesia dalam versi 12TL Sedan, 12TL Station wagon antara tahun 1973 dan 1977. Model facelift 12TS S…

Florentia, Captn Wimble. Passing through Telleberry Roads, off the coast of Malabar 1 February 1825 History United Kingdom NameFlorentia BuilderNewcastle upon Tyne Launched1821 General characteristics Tons burthen453 ton (bm) PropulsionSail Florentia was a 453-ton merchant ship built at Newcastle upon Tyne, England in 1821. She made one voyage transporting convicts from England to Australia and one voyage from Ireland to Australia. She made three voyages for the British East India Company (EIC).…
كأس جورجيا 2017 تفاصيل الموسم كأس جورجيا النسخة 28 البلد جورجيا التاريخ بداية:2 مارس 2017 نهاية:2 ديسمبر 2017 المنظم اتحاد جورجيا لكرة القدم البطل نادي تشيخورا ساتشخيره مباريات ملعوبة 73 عدد المشاركين 80 كأس جورجيا 2016 كأس جورجيا 2018 تعديل مصدري - تع�…

American baseball player (1925-2011) Baseball player Bob RushPitcherBorn: (1925-12-21)December 21, 1925Battle Creek, Michigan, U.S.Died: March 19, 2011(2011-03-19) (aged 85)Mesa, Arizona, U.S.Batted: RightThrew: RightMLB debutApril 22, 1948, for the Chicago CubsLast MLB appearanceAugust 7, 1960, for the Chicago White SoxMLB statisticsWin–loss record127–152Earned run average3.65Strikeouts1,244 Teams Chicago Cubs (1948–1957) Milwaukee Braves (1958–1960) C…


