Ronald Clark O'Bryan
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Laman ini adalah tentang unit militer. Untuk artikel tentang gerakan kaum muda, mohon lihat Kepanduan Pemuda Filipina. Kepanduan FilipinaLambang unit Kepanduan Filipina dari 1921-1947 adalah kepala carabao (kerbau air) yang melambangkan Filipina. Warna merah dan emas mewakili akar kolonial Spanyol di kepulauan tersebut.Aktif1901–1948Negara Amerika Serikat FilipinaAliansi Amerika Serikat(1901–1946) Pemerintahan Insular(1901–1935) Persemakmuran Filipina(1935–1946) Temp…

Artikel ini memiliki beberapa masalah. Tolong bantu memperbaikinya atau diskusikan masalah-masalah ini di halaman pembicaraannya. (Pelajari bagaimana dan kapan saat yang tepat untuk menghapus templat pesan ini) Artikel ini membutuhkan penyuntingan lebih lanjut mengenai tata bahasa, gaya penulisan, hubungan antarparagraf, nada penulisan, atau ejaan. Anda dapat membantu untuk menyuntingnya. Kontributor utama artikel ini tampaknya memiliki hubungan dekat dengan subjek. Artikel ini mungkin memerluka…

Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article ne cite pas suffisamment ses sources (mars 2009). Si vous disposez d'ouvrages ou d'articles de référence ou si vous connaissez des sites web de qualité traitant du thème abordé ici, merci de compléter l'article en donnant les références utiles à sa vérifiabilité et en les liant à la section « Notes et références » En pratique : Quelles sources sont attendues ? Comment …

Voce principale: Viareggio Calcio. Associazione Sportiva Calcio ViareggioStagione 1993-1994Sport calcio Squadra Viareggio Allenatore Massimo Morgia poi Aldo Cerantola Presidente Franco Corbelli poi Maria Sonia Favaro Serie C27º posto nel girone B. Non ammesso alla stagione 1994-95 per problemi finanziari. Coppa Italia Serie CFase a gironi Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Scarponi (32) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Lugnan (5) StadioStadio Torquato Bresciani 1992-1993 1994-1995 Si invita a seguir…
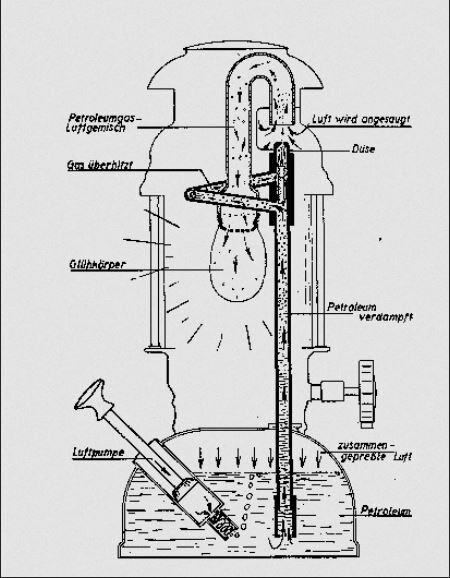
Informasi lebih lanjut: Petromaks (disambiguasi) Petromaks adalah sejenis alat penerangan (lampu) yang menggunakan bahan bakar minyak tanah bertekanan, dan dalam menyalakannya dibantu dengan spiritus (kerosin, parafin). Desain lampu ini ditemukan pada tahun 1910 oleh Max Graetz (1851-1937), CEO dari perusahaan Ehrich & Graetz, yang berpusat di Berlin. Nama Petromax sendiri merupakan gabungan kata dari “Petroleum” dan “Max Graetz”. Nama Petromax yang awalnya merupakan merek dagang, ka…

K-Love radio station in Santa Fe, New Mexico For the airport in Suffolk, Virginia assigned the ICAO code KSFQ, see Suffolk Executive Airport. KQLVSanta Fe, New MexicoBroadcast areaSanta Fe/ Albuquerque areasFrequency90.7 (MHz)BrandingK-LoveProgrammingFormatChristian ContemporaryAffiliationsK-LoveOwnershipOwnerEducational Media FoundationSister stationsKQRI, KQGCHistoryFirst air date1987Former call signsKSFR (1987–2007)KSFQ (2007–2009)Technical informationClassCERP19,810 wattsHAAT1,261 meters…

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、蘭&…

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、蘭&…

Civilian who undertakes law enforcement without legal authority Vigilante redirects here. For other uses, see Vigilante (disambiguation). The Bald Knobbers, an 1880s vigilante group from Missouri – as portrayed in the 1919 film The Shepherd of the Hills Vigilantism (/vɪdʒɪˈlæntɪzəm/) is the act of preventing, investigating and punishing perceived offenses and crimes without legal authority.[1][2] A vigilante is a person who practices or partakes in vigilantism, or un…

1927 film by Edmund Goulding LoveDirected byEdmund GouldingJohn GilbertWritten byLorna MoonFrances MarionMarian AinsleeRuth CummingsBased onAnna Karenina1876 novelby Leo TolstoyProduced byEdmund GouldingStarringJohn GilbertGreta GarboCinematographyWilliam H. DanielsEdited byHugh WynnMusic byArnold Brostoff (1944)Distributed byMetro-Goldwyn-MayerRelease date November 27, 1927 (1927-11-27) [1]Running time82 minutesCountryUnited StatesLanguagesSilent filmSound film 1928 Relea…

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年5月6日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 约翰斯顿环礁Kalama Atoll 美國本土外小島嶼 Johnston Atoll 旗幟颂歌:《星條旗》The Star-Spangled Banner約翰斯頓環礁地�…

American Hockey League championship trophy Not to be confused with Calder Memorial Trophy. Calder CupSportIce hockeyCompetitionCalder Cup playoffsAwarded forWinner of the American Hockey League playoffsHistoryFirst award1937First winnerSyracuse Stars (1)Most winsHershey Bears (12)Most recentHershey Bears (12) The Calder Cup is the trophy awarded annually to the playoff champions of the American Hockey League. It was first presented in 1937 to the Syracuse Stars.[N 1] The cup is made of s…

Kádár János人名顺序为先姓后名。本条目中的译名遵从此顺序。 卡达尔·亚诺什Kádár János匈牙利社会主义工人党第一书记任期1956年10月25日—1988年5月22日(31年210天)前任格罗·埃诺继任格罗斯·卡罗伊匈牙利人民共和国部长会议主席任期1956年11月4日—1958年1月28日(1年85天)前任纳吉·伊姆雷继任明尼赫·费伦茨任期1961年9月13日—1965年6月3日(3年263天)前任明尼赫·费伦茨继任…

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Union pour un mouvement populaire (homonymie), UMP, Union populaire et Union pour la majorité présidentielle. Union pour un mouvement populaire Logotype officiel. Présentation Fondation 23 avril 2002(Union pour la majorité présidentielle)17 novembre 2002(Union pour un mouvement populaire) Fusion de RPRDLMDRUDF (dissidents) Scission dans DLR (2008) Siège 238, rue de Vaugirard75015 Paris Cedex 15 Changement de nom 30 mai 2015 (devenue Les Républicains) Pers…

Cristian Boscolo Nazionalità Italia Calcio Ruolo Centrocampista Termine carriera 2009 CarrieraSquadre di club1 1990-1996 Como89 (1)1996-1997→ Lecco13 (1)1996-1997 Como10 (0)1997-2001 Lumezzane120 (0)2001-2002 Mantova31 (0)2002-2006 Pro Patria120 (0)2006-2007 Pro Sesto17 (0)2007-2009 Pergocrema54 (0) 1 I due numeri indicano le presenze e le reti segnate, per le sole partite di campionato.Il simbolo → indica un trasferimento in prestito. Mo…

Thiazide-like diuretic drug ChlortalidoneClinical dataTrade namesHygroton, Thalitone, othersAHFS/Drugs.comMonographMedlinePlusa682342License data US DailyMed: Chlorthalidone Pregnancycategory AU: C Routes ofadministrationBy mouthDrug classThiazide-like diureticATC codeC03BA04 (WHO) Legal statusLegal status UK: POM (Prescription only) US: ℞-only Pharmacokinetic dataProtein binding75%Elimination half-life40 hoursExcretionKidneyIdentifiers IUPAC name (RS)-2-Chlo…

1950 Indonesian war film by Usmar Ismail Darah dan DoaMagazine advertisement, Aneka (1 September 1950)Directed byUsmar IsmailWritten by Usmar Ismail Sitor Situmorang Produced byUsmar IsmailStarring Del Juzar Ella Bergen Aedy Moward Awaluddin Djamin CinematographyMax TeraEdited byDjohan SjafriMusic byG. R. W. SinsuProductioncompanyPerfiniDistributed bySpectra Film ExchangeRelease date 1950 (1950) Running time128 minutesCountryIndonesiaLanguageIndonesianBudget350,000 rupiah Darah dan Doa ( …

The list of snowiest places in the United States by state shows average annual snowfall totals for the period from mid-1985 to mid-2015. Only places in the official climate database of the National Weather Service, a service of NOAA, are included in this list. Some ski resorts and unofficial weather stations report higher amounts of snowfall than places on this list. Official weather stations are usually located in populated places and snowfall statistics for isolated and unpopulated areas are o…

Item that is not new being sold or transferred Second hand and Hand me down redirect here. For other uses, see second hand (disambiguation). For the Kate Rusby album, see Hand Me Down. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Used good – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2021) (Learn how…

Tactic employed in response to an attack For other uses, see Counterattack (disambiguation). Closing the Falaise-Argentan Pocket and the Mortain counterattack 6–17 August 1944 Map of the Battle of Cambrai – German counter-offensive A counterattack is a tactic employed in response to an attack, with the term originating in war games.[1] The general objective is to negate or thwart the advantage gained by the enemy during attack, while the specific objectives typically seek to regain l…

