Second Iraqi–Kurdish War
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: 2016 Pasig local elections – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) 2016 Pasig mayoral election ← 2013 May 9, 2016 (2016-05-09) 2019 → Nominee Rob…
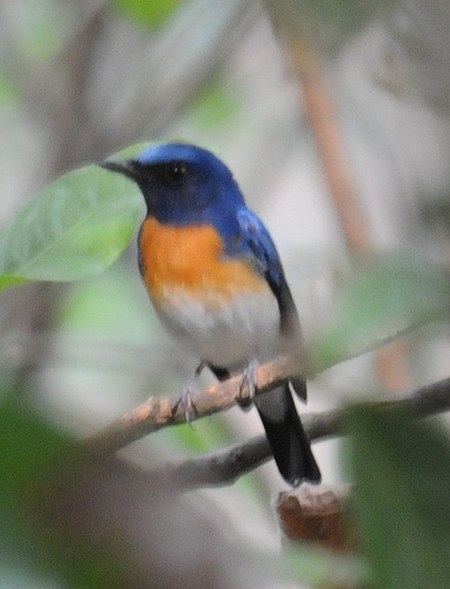

Cyornis Cyornis Blue-throated blue flycatcher (C. rubeculoides)TaksonomiKerajaanAnimaliaFilumChordataKelasAvesOrdoPasseriformesFamiliMuscicapidaeGenusCyornis Blyth, 1843 Tata namaSinonim taksonRhinomyias Sharpe, 1879lbs Tledekan atau sulingan adalah sejenis burung pengicau dari genus Cyornis, genus burung dalam keluarga sikatan Dunia Lama Muscicapidae yang sebagian besar berasal dari Asia Tenggara.Walau begitu, beberapa spesies lainnya juga disebut sebagai sikatan. Jenis Tledekan Hainan ( C…

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article may require cleanup to meet Wikipedia's quality standards. The specific problem is: much of the article is listing properties and facts with no context. Please help improve this article if you can. (May 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) This article is an orphan, as no other articles link to it. Please intr…

Overview of the environmental issues in the Philippines Today, environmental problems in the Philippines include pollution, mining and logging, deforestation, threats to environmental activists, dynamite fishing, landslides, coastal erosion, biodiversity loss, extinction, global warming and climate change.[1][2][3] Due to the paucity of extant documents, a complete history of land use in the archipelago remains unwritten. However, relevant data shows destructive land use …

Aad de Mos Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Adriaan de MosTanggal lahir 27 Maret 1947 (umur 76)Tempat lahir Den Haag, BelandaKepelatihanTahun Tim 1999 Urawa Reds Adriaan Aad de Mos (lahir 27 Maret 1947) adalah mantan pelatih sepak bola dan adalah mantan pemain sepak bola asal Belanda. Pranala luar (Jepang) J. League Data Site Wikimedia Commons memiliki media mengenai Aad de Mos. Artikel bertopik pemain sepak bola Belanda ini adalah sebuah rintisan. Anda dapat membantu Wikipedia dengan mengemba…

Lunar Prospector adalah misi ketiga yang dipilih oleh NASA untuk pengembangan penuh dan konstruksi sebagai bagian dari Program Discovery. Dengan biaya $ 62.800.000, misi 19 bulan dirancang untuk orbit polar investigasi rendah dari bulan, termasuk pemetaan komposisi permukaan dan kemungkinan deposito es di kutub, pengukuran medan magnet dan gravitasi, dan studi peristiwa outgassing lunar. Misi yang berakhir 31 Juli 1999, ketika pengorbit itu sengaja menabrak kawah di dekat kutub selatan bulan set…

Kardinal Pietro Ottoboni, dilukis oleh Francesco Trevisani. Museum Bowes, Kastel Barnard, County Durham, Inggris. Pietro Ottoboni (2 Juli 1667 – 29 Februari 1740) adalah seorang kardinal Italia dan anak dari keponakan Paus Aleksander VIII (yang juga memiliki nama lahir Pietro Ottoboni). Ia secara khusus diingat sebagai pelindung musik dan kesenian. Ottoboni adalah orang terakhir yang memegang jabatan Kardinal keponakan, yang kemudian dihapuskan oleh pengganti Aleksander VIII, Paus Innosensius …

PotensiometerPotensiometer satu putaran yang umumSimbol (EU) (US)TipeKomponen pasifKategoriKomponen resistiflbs Potensiometer adalah resistor tiga terminal dengan sambungan geser yang membentuk pembagi tegangan dapat disetel.[1] Jika hanya dua terminal yang digunakan (salah satu terminal tetap dan terminal geser), potensiometer berperan sebagai resistor variabel atau Rheostat. Potensiometer biasanya digunakan untuk mengendalikan peranti elektronik seperti pengendali suara pada penguat. P…

It's Me (Pick Me)Singel oleh Produce 101 Season 2 contestantsDirilis9 Maret 2017FormatUnduh digitalDirekam2017GenreK-popdance-popelectropopEDMDurasi4:07LabelCJ E&MPenciptaRyan S. JhunEmile GhantousKeith HetrickAppu KrishnanCheryline LimJason JonesZaydroRHeaT It's Me (Pick Me) adalah sebuah lagu oleh peserta program survival Korea Selatan, Produce 101 Season 2. Lagu ini dirilis sebagai singel digital pada 9 Maret 2017 oleh CJ E&M. Daftar lagu No.JudulLirikMusikDurasi1.It's Me (Pick Me)Rya…

Justin PrenticeLahir25 Maret 1994 (umur 29)PekerjaanAktorTahun aktif2010–sekarang Justin Prentice (lahir 25 Maret 1994) adalah aktor asal Amerika Serikat. Prentice dikenal karena perannya dalam beberapa serial televisi Amerika Serikat, namun yang paling dikenal melalui serial Netflix, 13 Reasons Why sebagai Bryce Walker.[1] Filmografi Film Tahun Judul Peran Catatan 2011 Terri Dirty Jack 2015 Sex, Death and Bowling Rick Remaja 2017 Brownstone Luke Televisi Tahun Judul Peran Ca…

Canadian non-profit organization The Victorian Order of Nurses (VON) has been leading home and community care in Canada for over a century. Today, VON provides home and community support services to over 10,000 people every day across Ontario and Nova Scotia. It is registered as a charity with the Canada Revenue Agency, under charity number 129482493RR0001.[1] Since 2014, the President and CEO is Jo-Anne Poirier. History Founder Lady Aberdeen was the first woman to receive an honorary de…
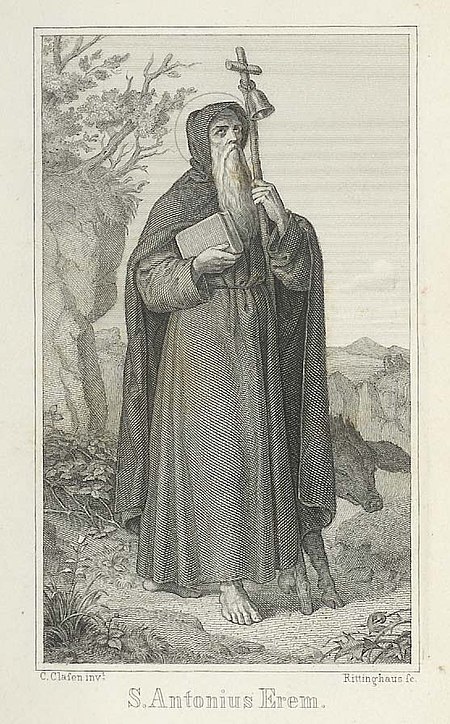

Antonius, pendiri ordo kerahiban Antonius lahir di Mesir sekitar tahun 250, dalam keluarga kaya. Ketika ia berumur dua puluh tahun, orang tuanya wafat, meninggalkan seluruh harta untuknya. Mengikuti petunjuk Yesus, ia membagikan tanah miliknya kepada orang-orang sekampung, menjual harta lainnya dan menyumbangkan uangnya kepada orang-orang miskin. Ia berguru pada seorang Kristen yang sudah berumur, dan belajar tentang sukacita penyangkalan diri. Antonius makan hanya satu kali sehari, yang terdiri…

Artikel ini tidak memiliki bagian pembuka yang sesuai dengan standar Wikipedia. Mohon tulis paragraf pembuka yang informatif sehingga pembaca dapat memahami maksud dari Gangguan tidur. Contoh paragraf pembuka Gangguan tidur adalah .... (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) Artikel ini memberikan informasi dasar tentang topik kesehatan. Informasi dalam artikel ini hanya boleh digunakan untuk penjelasan ilmiah; bukan untuk diagnosis diri dan tidak dapat menggantikan d…
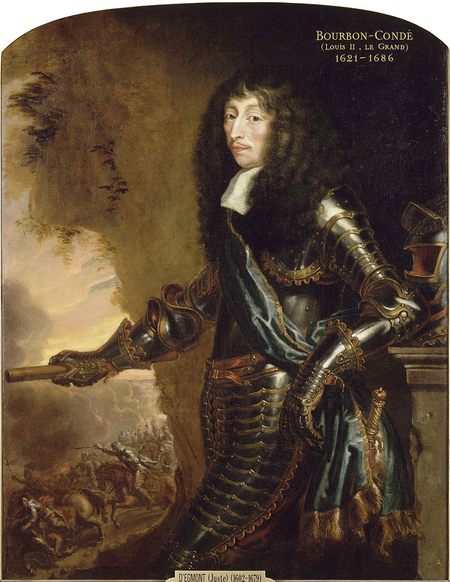

Louis II dari Bourbon-CondéNama dalam bahasa asli(fr) Louis II de Bourbon-Condé BiografiKelahiran8 September 1621 Paris Kematian11 Desember 1686 (65 tahun)Fontainebleau Data pribadiAgamaGereja Katolik Roma KegiatanPekerjaanCondottiero dan personel militer Periode aktif1643 –Cabang militerAngkatan darat Pangkat militerJenderal KonflikPerang Tiga Puluh Tahun dan Perang Perancis–Spanyol Lain-lainGelar bangsawanDuke KeluargaWangsa Bourbon Pasangan nikahClaire-Clémence de Maillé-Brézé…
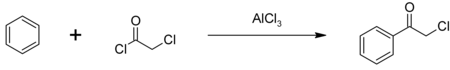
Kloroasetil klorida Nama Nama IUPAC (preferensi) Kloroasetil klorida Nama lain 2-Kloroasetil kloridaKloroasetil asam kloridaKloroasetil kloridaMonokloroasetil klorida Penanda Nomor CAS 79-04-9 Y Model 3D (JSmol) Gambar interaktif 3DMet {{{3DMet}}} ChemSpider 13856283 N Nomor EC KEGG C14859 Y PubChem CID 6577 Nomor RTECS {{{value}}} CompTox Dashboard (EPA) DTXSID4026472 InChI InChI=1S/C2H2Cl2O/c3-1-2(4)5/h1H2 NKey: VGCXGMAHQTYDJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N NInChI=1/C2H2Cl2O/c3-1-2…

H.GamalisS.E. Wakil Bupati Berau ke-4PetahanaMulai menjabat 26 Februari 2021PresidenJoko WidodoGubernurIsran NoorBupatiSri Juniarsih Mas PendahuluAgus TantomoPenggantiPetahana Informasi pribadiLahir11 November 1966 (umur 57)Tanjung Redeb, Kalimantan TimurKebangsaanIndonesiaPartai politikPPPSuami/istriHj. Sri Aslinda Sulaiman, S.H.Anak4Alma materUniversitas Negeri MalangPekerjaanPolitikusSunting kotak info • L • B H. Gamalis, S.E. (lahir 11 November 1966) adalah Wakil B…

Basilika Bunda BiaraBasilika Minor Bunda BiaraPortugis: Basilica de Nossa Senhora da Abadiacode: pt is deprecated Basilika Bunda BiaraLokasiUberabaNegara BrasilDenominasiGereja Katolik RomaArsitekturStatusBasilika minorStatus fungsionalAktif Basilika Bunda Biara (Portugis: Basilica de Nossa Senhora da Abadiacode: pt is deprecated ) adalah sebuah gereja basilika minor Katolik yang terletak di Uberaba, Brasil. Basilika ini ditetapkan statusnya pada tahun 2020 dan didedikasikan kepada Bunda Bi…

BiskekБишкек Capital BanderaEscudo BiskekLocalización de Biskek en Kirguistán BiskekLocalización de Biskek en AsiaCoordenadas 42°52′00″N 74°34′00″E / 42.866666666667, 74.566666666667Idioma oficial kirguís y rusoEntidad Capital • País Kirguistán Kirguistán • Óblast ChuyDirigentes • Alcalde Aibek JunushalievSubdivisiones 4 raionesEventos históricos • Fundación 1825 • Creación 1878Superficie • …
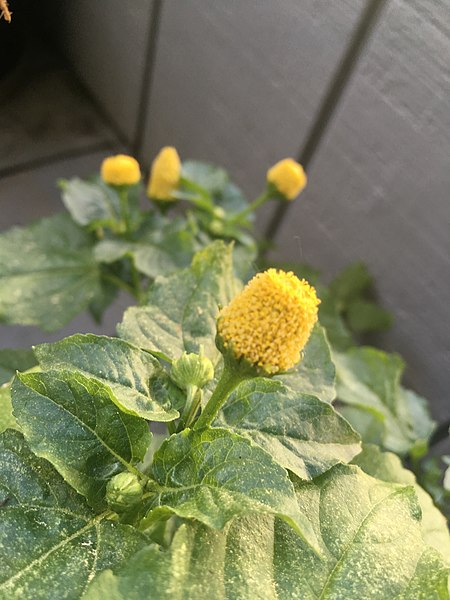

Acmella acmella alba Klasifikasi ilmiah Domain: Eukaryota Kerajaan: Plantae Upakerajaan: Trachaeophyta Divisi: Magnoliophyta Kelas: Magnoliopsida Subkelas: Asteridae Ordo: Asterales Famili: Asteraceae Subfamili: Asteroideae Tribus: Heliantheae Subtribus: Spilanthinae Genus: AcmellaRich. ex Pers. Spesies tipe Acmella repens(Walter) Rich.[1][2] Spesies Lihat teks Sinonim[2] Spilanthes section Acmella (Pers.) DC. Athronia Neck Acmella adalah salah satu genus tumbuhan berbung…

Ini adalah nama Tionghoa; marganya adalah Zhang (Chang). Zhang Junmai Zhang Junmai (Hanzi: 张君劢; Wade–Giles: Chang Chun-mai; 1886–1969), juga dikenal dalam dialek Shanghai dengan nama lahirnya Carsun Chang (Hanzi: 張嘉森; Pinyin: Zhāng Jiāsēn) adalah seorang filsuf, intelektual publik dan figur politik asal Tiongkok. Zhang Junmai adalah seorang politikus sosial demokrat.[1] Referensi ^ Jeans Jr. (1997), hlm. 41. Karya Chang, Carsun. The Third Force in …
