Spektr-R
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
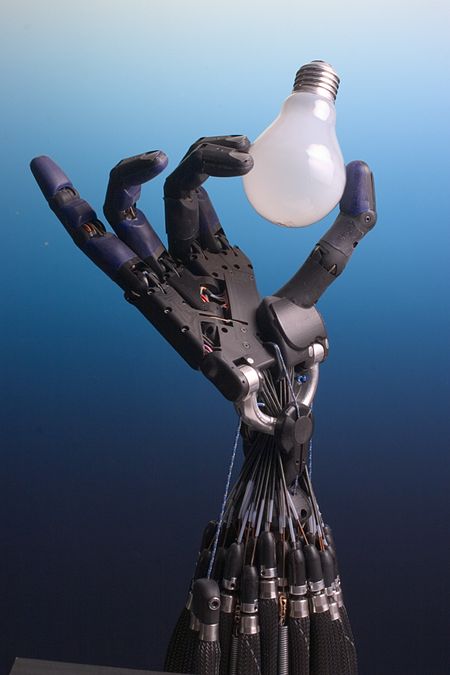

Robot di pabrik Sistem tangan robot Robotika adalah satu cabang teknologi yang berhubungan dengan desain, konstruksi, operasi, disposisi struktural, pembuatan, dan aplikasi dari robot.[1] Robotika terkait dengan ilmu pengetahuan bidang elektronika, mesin, mekanika, dan perangkat lunak komputer.[2] Pemikiran tentang pembuatan mesin yang dapat bekerja sendiri telah ada sejak Era Klasik, tetapi riset mengenai penggunaannya tidak berkembang secara berarti sampai abad ke-20.[3]…
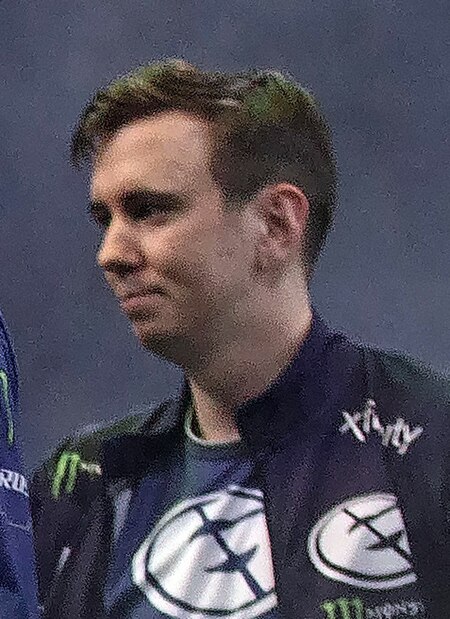

Gustav MagnussonMagnusson, 2018StatusAktifTanggal lahir1 April 1992 (umur 31)Tempat tinggalStockholm, SwediaKebangsaan SwediaTim saat iniAlliancePermainanDota 2Riwayat karir2013–2014Alliance2014–2015Team Secret2015Alliance2016–2018OG2018–2019Evil Geniuses2020–kiniAlliance Pencapaian dan penghargaan Pemenang The International (2013) Pemenang 2× Dota Major (Boston, Kiev) Gustav Magnusson (lahir 1 April 1992), lebih dikenal dengan nama s4, adalah seorang pemain profesional Dota…
Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada September 2015. Pantai Carnaval adalah salah satu pantai yang ada di Taman Impian Jaya Ancol, Jakarta. Pantai yang memiliki ruang terbuka yang cukup luas, disini ada Ancol Beach City. Pada tahun 2022, Formula E diadakan disini. dan beberapa kali masuk rekor Museum Reko…

Adrià Pedrosa Pedrosa with Espanyol in 2019Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Adrià Giner PedrosaTanggal lahir 13 Mei 1998 (umur 25)Tempat lahir Barcelona, SpainTinggi 172 m (564 ft 4 in)Posisi bermain Left backInformasi klubKlub saat ini EspanyolNomor 3Karier junior2004–2009 Castelldefels2009–2014 Gavà2014–2017 EspanyolKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2017–2018 Espanyol B 46 (7)2018– Espanyol 23 (2)Tim nasional‡2019– Spanyol U-21 4 (1) * Penampilan dan gol di …

Keuskupan RožňavaDioecesis RosnaviensisDieceze RoznavskaKatolik Lambang keuskupanLokasiNegaraSlowakiaProvinsi gerejawiKeuskupan Agung KošiceStatistikLuas7.000 km2 (2.700 sq mi)Populasi- Total- Katolik(per 2014)390.584205,431 (52.6%)InformasiDenominasiKatolik RomaPendirian13 Maret 1776KatedralGereja Kenaikan Maria (Rožňava)Kepemimpinan kiniPausFransiskusUskupStanislav Stolárik[1][2]PetaPeta keuskupan Keuskupan Rožňava (bahasa Slowakia:…
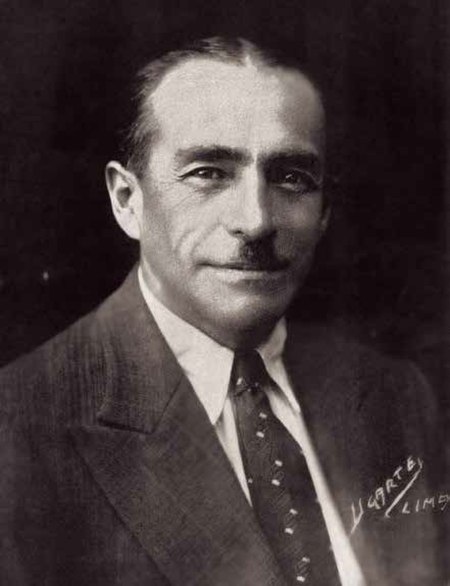

Gustavo Jiménez Gustavo Jiménez (lahir di Cerro de Pasco, Pasco, tahun 1886 - meninggal di Paiján, La Libertad, 14 Maret 1933) adalah seorang kolonel Peru yang menjabat sebagai Presiden Peru selama enam hari pada tahun 1931. Jiménez mengorganisir salah satu dari beberapa pemberontakan yang menyebabkan jatuhnya pemerintahan Augusto B. Leguía. Setelah pencalonan Jenderal Luis Miguel Sánchez Cerro sebagai presiden sementara yang baru, Jiménez terus mendukung hal itu meski ia tidak setuju den…

إن تخليق اليوريا (والمواد العضوية الأخرى) من المركبات غير العضوية كانت تدحض فرضية vitalist وهي أن الكائنات الحية فقط يمكن أن تخلق هذه المركبات . المذهب الحيوي هو الاعتقاد بأن «الكائنات الحية تختلف اختلافًا جوهريًا عن الكيانات غير الحية لأنها تحتوي على بعض العناصر غير المادية أو …

Miss VenezuelaTanggal pendirian1952TipeKontes kecantikanKantor pusatCaracas, VenezuelaLokasi VenezuelaJumlah anggota Miss UniverseMiss WorldMiss InternationalBahasa resmi Bahasa SpanyolPresidenOsmel SousaSitus webSitus web resmi Miss Venezuela adalah kontes kecantikan yang diadakan di Venezuela sejak tahun 1952.[1] Kontes ini diselenggarakan untuk memilih wakil Venezuela di kontes kecantikan Miss Universe, Miss World, dan Miss International. Sejak tahun 2013, kontes ini dipecah menj…

Cet article est une ébauche concernant un zoologiste ou un botaniste. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Consultez la liste des tâches à accomplir en page de discussion. Hermann zu Solms-LaubachBiographieNaissance 23 décembre 1842LaubachDécès 24 novembre 1915 (à 72 ans)StrasbourgNationalité hessoiseFormation Université Martin-Luther de Halle-WittembergActivités Botaniste, paléontologue, …
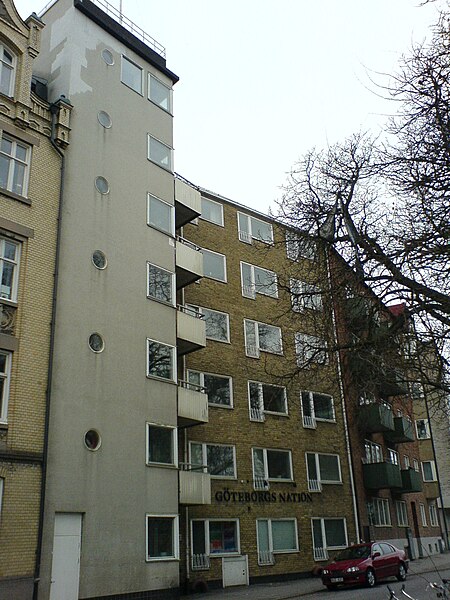

Student society in Lund, Sweden Not to be confused with Göteborgs nation, Uppsala.Göteborgs NationStudent nationLund UniversityGöteborg Nation's nation house LocationÖstra Vallgatan 47, Lund, SwedenLatin nameNatio GothoburgensisAbbreviationGBFounded1682NamesakeGothenburg, SwedenInspektorAndreas IngehammarProinspektorMonica LarsdotterMembershi…

Voce principale: Associazione Sportiva Dilettantistica Civitavecchia Calcio 1920. Associazione Calcio CivitavecchiaStagione 1978-1979Sport calcio Squadra Civitavecchia Allenatore Roberto Melchiorri poi Nicola Petrovic Presidente Giovanni Fattori Serie C28º posto nel girone A. Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Parasmo (34) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Fallone (5) 1977-1978 1979-1980 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa pagina raccoglie le informazioni riguardanti l'Associazione Calcio C…

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع بارانا (توضيح). بارانا - Paraná بارانا (ولاية) الموقع الجغرافي سميت باسم نهر بارانا تاريخ التأسيس 1889 تقسيم إداري البلد البرازيل[1][2] العاصمة كوريتيبا بارانا خصائص جغرافية إحداثيات 24°40′S 51°37′W / 24.67°S 51.62°W / -24.67; -51.62 […

Anglo-Irish physician, naturalist and collector (1660–1753) This article is about the physician and collector. For the Member of Parliament, see Hans Sloane (MP). SirHans SloaneBt FRSPortrait by Stephen Slaughter13th President of the Royal SocietyIn office1727–1741Preceded byIsaac NewtonSucceeded byMartin FolkesPresident of the Royal College of PhysiciansIn office1719–1735Preceded byJohn BatemanSucceeded byThomas Pellett Personal detailsBorn(1660-04-16)16 April 1660Killyleagh, Irel…

Damiano Longhi Longhi al Padova nel 1990 Nazionalità Italia Altezza 173 cm Peso 69 kg Calcio Ruolo Allenatore (ex centrocampista) Squadra Padova Termine carriera 2002 - giocatore Carriera Giovanili 1982-1984 Modena Squadre di club1 1984-1987 Modena77 (4)1987-1989 Padova60 (3)1989-1990 Pescara36 (0)1990-1996 Padova204 (22)1996-1997 Hércules13 (0)1997 Reggiana13 (0)1997-1998 Castel di Sangro28 (9)1998-2001 Treviso49 (2)2002 Fiorenzuola2 (0)…

Рабулеилат. Rabuleii Подданство Древний Рим Гражданская деятельность децимвир, народный трибун Военная деятельность полководец Рабулеи (лат. Rabuleii, gens Rabuleia) — древний римский род, очевидно, имевший и патрицианскую, и плебейскую ветви. Деятельность известных представител…

Brazilian footballer (born 1971) In this Portuguese name, the first or maternal family name is de Paula and the second or paternal family name is Nunes. Paulo Nunes Personal informationFull name Arílson de Paula NunesDate of birth (1971-10-30) 30 October 1971 (age 52)Place of birth Pontalina, BrazilHeight 1.74 m (5 ft 9 in)Position(s) Second strikerYouth career FlamengoSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)1991–1994 Flamengo 45 (30)1995–1997 Grêmio 44 (27)1997 Benfica …

ХристианствоБиблия Ветхий Завет Новый Завет Евангелие Десять заповедей Нагорная проповедь Апокрифы Бог, Троица Бог Отец Иисус Христос Святой Дух История христианства Апостолы Хронология христианства Раннее христианство Гностическое христианство Вселенские соборы Ни�…

「俄亥俄」重定向至此。关于其他用法,请见「俄亥俄 (消歧义)」。 俄亥俄州 美國联邦州State of Ohio 州旗州徽綽號:七葉果之州地图中高亮部分为俄亥俄州坐标:38°27'N-41°58'N, 80°32'W-84°49'W国家 美國加入聯邦1803年3月1日,在1953年8月7日追溯頒定(第17个加入联邦)首府哥倫布(及最大城市)政府 • 州长(英语:List of Governors of {{{Name}}}]]) • …

British independent think tank Institute for GovernmentFormation2008TypeThink tankHeadquarters2 Carlton Gardens, London, SW1Y 5AALocationLondon, EnglandDirectorHannah WhiteWebsitewww.instituteforgovernment.org.uk Carlton Gardens The Institute for Government (IfG[1]) is a British independent think tank which aims to improve government effectiveness through research and analysis. Based at 2 Carlton Gardens in central London and founded as a charity in 2008,[2] it was initially fund…

SMK Negeri 8 JakartaInformasiDidirikan30 September 1965 [1]AkreditasiA (Unggul)[2]Nomor Pokok Sekolah Nasional20102597Kepala SekolahDrs. Dadan Sabrudin M.M.Jurusan atau peminatanBisnis Manajemen dan PariwisataRentang kelasX-XIIKurikulumKurikulum 2013 RevisiJumlah siswa1.060 Peserta DidikStatusSekolah Menengah Kejuruan NegeriAlamatLokasiJl. Pejaten Raya, Kompleks Depdikbud, RT.07/RW.06, Pejaten Barat, Jakarta Selatan, DKI Jakarta, IndonesiaTel./Faks.(021) 7996493Ko…


