Bengali Brahmin
| |||||||||||||
Read other articles:

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2018年3月17日)请协助補充多方面可靠来源以改善这篇条目,无法查证的内容可能會因為异议提出而被移除。致使用者:请搜索一下条目的标题(来源搜索:羅生門 (電影) — 网页、新闻、书籍、学术、图像),以检查网络上是否存在该主题的更多可靠来源(判定指引)。 此�…

Asakuchi 浅口市Kota BenderaLambangLokasi Asakuchi di Prefektur OkayamaNegara JepangWilayahChūgokuPrefektur OkayamaPemerintahan • Wali kotaYasuhiko KuriyamaLuas • Total66,5 km2 (257 sq mi)Populasi (Oktober 1, 2015) • Total34.235 • Kepadatan514,8/km2 (13,330/sq mi)Zona waktuUTC+9 (JST)Kode pos719-0295Simbol • PohonPrunus serrulataNomor telepon0865-44-7000Alamat3050 Kamogatachōrokujōinnaka, Asakuchi…

This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: Extract, load, transform – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2023) Extract, load, transform (ELT) is an alternative to extract, transform, load (ETL) used with data lake implementations. In contrast to ETL, in ELT models the data is n…

Pulau Sentinel UtaraPencitraan udara oleh NASA pada tahun 2009. Menampilkan gambar Pulau Sentinel Utara, pulau terumbu karang yang mengelilingi pulau terlihat dengan jelas.Pulau Sentinel UtaraGeografiKoordinat11°33′N 92°14′E / 11.550°N 92.233°E / 11.550; 92.233Koordinat: 11°33′N 92°14′E / 11.550°N 92.233°E / 11.550; 92.233[1]KepulauanKepulauan Andaman[2]Luas72 km2[2]Titik tertinggi122 m[1&#…

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Gusti – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Gusti adalah gelar kebangsawanan yang umumnya dimiliki oleh kerajaan-kerajaan di Indonesia yang mendapat pengaruh dari kerajaan-kerajaan (Bahasa Jaw…

Об экономическом термине см. Первородный грех (экономика). ХристианствоБиблия Ветхий Завет Новый Завет Евангелие Десять заповедей Нагорная проповедь Апокрифы Бог, Троица Бог Отец Иисус Христос Святой Дух История христианства Апостолы Хронология христианства Ранне…

German football club Football clubSC Weiche Flensburg 08Full nameSportclub Weiche Flensburg von 1908 e.V.Founded1908GroundManfred-Werner-StadionCapacity2,500ChairmanHans-Lothar SuhrManagerThomas SeeligerLeagueRegionalliga Nord (IV)2022–235th SC Weiche Flensburg 08 is a German association football club from the Weiche suburb of Flensburg, Schleswig-Holstein. Apart from football the club also offers other sports like volleyball and table tennis. Before July 2017, the club was known as ETSV Weich…

Microsoft LyncLisensiPerangkat lunak uji coba Sunting di Wikidata • Sunting kotak info • L • BBantuan penggunaan templat ini Microsoft Lync (sebelumnya bernama Office Communicator) adalah perangkat lunak perkantoran yang termasuk dalam bundel Microsoft Office. Microsoft Lync berasal dari dua kata, yaitu link (artinya menggabungkan) dan sync (artinya menyinkronkan).[1] Kegunaan Microsoft Lync digunakan sebagai aplikasi perpesanan instan yang ditujukan untuk bisnis.Ca…

For battles in the same place or in the surroundings, see Battle of Nassau. Capture of the BahamasPart of the American Revolutionary WarMap of the BahamasDateMay 1782LocationNassau, Bahamas25°03′35.84″N 77°20′42.06″W / 25.0599556°N 77.3450167°W / 25.0599556; -77.3450167Result Spanish victoryBelligerents Great Britain SpainCommanders and leaders John Maxwell Juan Manuel Cagigal y Monserrat Francisco de MirandaStrength 23 ships1,400+[1] 59 sh…

Lukisan John Evelyn oleh Sir Godfrey Kneller, 1687. John Evelyn (31 Oktober 1620 – 27 Februari 1706) adalah seorang penulis Inggris, tukang kebun, dan penulis buku harian (diaris). Buku harian Evelyn atau Memoar yang ditulisnya sebagian besar bersifat kontemporer dan setipe dengan penulis buku harian Inggris lainnya seperti Samuel Pepys. Buku hariannya memberikan pengaruh yang besar terhadap budaya, seni dan politik saat ia menyaksikan kematian Charles I dan Oliver Cromwell, terj…

Questa voce sull'argomento calciatori italiani è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Bruno Varalli Nazionalità Italia Calcio Ruolo Difensore Carriera Squadre di club1 1922-1927 Novara38 (0) 1 I due numeri indicano le presenze e le reti segnate, per le sole partite di campionato.Il simbolo → indica un trasferimento in prestito. Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Bruno V…

River in Germany IlmenauThe Ilmenau near UelzenLocationCountryGermanyStateLower SaxonyReference no.DE: 594Physical characteristicsSource • locationsource: confluence of the Gerdau and Stederau in Veerßen [de] (a district of Uelzen) • coordinates52°56′52″N 10°33′13″E / 52.947639°N 10.5536806°E / 52.947639; 10.5536806 • elevation35 m above sea level (NN) (Gerdau 70&…

DH.53 Humming Bird Role Ultralight monoplaneType of aircraft Manufacturer de Havilland First flight 2 October 1923[1] Primary user Royal Air Force Produced 1923–1924 Number built 15 The de Havilland DH.53 Humming Bird is a British single-seat, single-engine, low-wing monoplane light aircraft first flown in the 1920s. Design and development In response to the Daily Mail Light Aeroplane Competition of 1923 de Havilland built two DH.53s which were named Humming Bird and Sylvia II. Th…

Cet article est une ébauche concernant la philosophie et la religion. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Sub specie æternitatis (en latin : « sous l'aspect de l'éternité » ou encore, d'une façon moins littérale, « de toute éternité ») est une notion à la fois religieuse et philosophique qui remonte à l'herméneutique de la Torah. Développée par Spinoza, cette mé…

Álex Mumbrú Mumbrú con la divisa della Spagna Nazionalità Spagna Altezza 202 cm Peso 105 kg Pallacanestro Ruolo Allenatore (ex ala piccola) Termine carriera 2018 - giocatore CarrieraGiovanili SESE BarcelonaSquadre di club 1997-2002 Joventut Badalona107 (1.012)2002-2004 Real Madrid65 (616)2004-2006 Joventut Badalona65 (668)2006-2009 Real Madrid88 (776)2009-2018 Bilbao Berri299 (3.842)Nazionale 1998 Spagna U-222001-2013 Spagna113 (541)Carriera da allenatore 2018-…
Elezioni regionali in Basilicata del 1970 Stato Italia Regione Basilicata Legislatura I Affluenza 85,50% Seggi in Consiglio regionale DC 14 / 30 PCI 7 / 30 PSI 4 / 30 PSU 2 / 30 MSI 1 / 30 PLI 1 / 30 PSIUP 1 / 30 Distribuzione del voto per comune Presidenti della Giunta regionale: Vincenzo Verrastro (DC) - 1975 Le elezioni regionali in Basilicata del 1970 si tennero il 7-8 giugno. Risultati elettorali Liste Voti % Seggi Democrazia Cristiana (DC) 131.602 42,35 14 Partito Comunista Ita…

Rugby league team season 2021 Penrith Panthers seasonNRL Rank2nd (Premiers)2021 recordWins: 21; draws: 0; losses: 3Points scoredFor: 676; against: 286Team informationCEOBrian FletcherCoachIvan ClearyCaptainNathan Cleary & Isaah YeoStadiumBlueBet Stadium – 22,500Carrington Park – 13,000 (round 8 only)Avg. attendance11,649High attendance20,890Top scorersTriesMatt Burton (16)GoalsNathan Cleary (88)PointsNathan Cleary (219) ← 2020 List of seasons 2022 →…
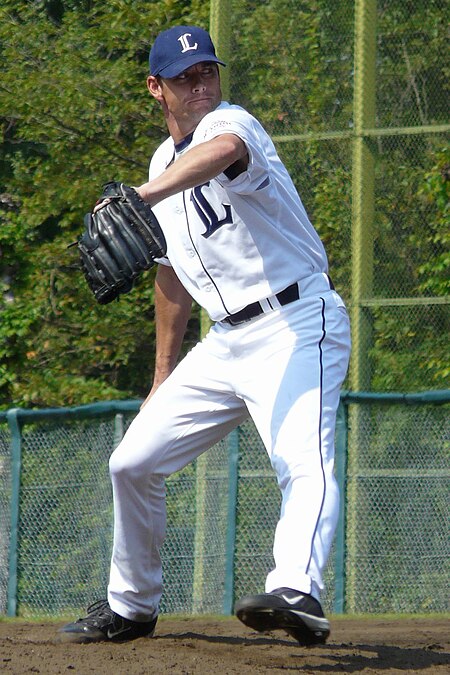

American baseball player (born 1972) Baseball player John WasdinWasdin with the Saitama Seibu LionsPitcherBorn: (1972-08-05) August 5, 1972 (age 51)Fort Belvoir, Virginia, U.S.Batted: RightThrew: RightProfessional debutMLB: August 24, 1995, for the Oakland AthleticsNPB: April 3, 2002, for the Yomiuri GiantsLast appearanceMLB: July 7, 2007, for the Pittsburgh PiratesNPB: August 13, 2009, for the Saitama Seibu LionsMLB statisticsWin�…

The former Erie Railroad station near the headquarters of the museum. The Railroad Museum of the Niagara Frontier is located in the 1922-built Erie Railroad freight depot in North Tonawanda, New York. Operated by the Niagara Frontier Chapter of the National Railroad Historical Society, its mission is to preserve the railroad history of the Buffalo, New York area, once the railroad hub of America.[1] The Museum is owned by the Niagara Frontier Chapter of the National Railway Historical So…

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Готы (значения). Готы Готический стиль в одежде Возникновение конец 1970-х Великобритания Годы расцвета 1980-е Направленность музыкальная Распространение ЕвропаАмерикаАзия Австралия Элементы Готическая музыкаГотическая мод�…