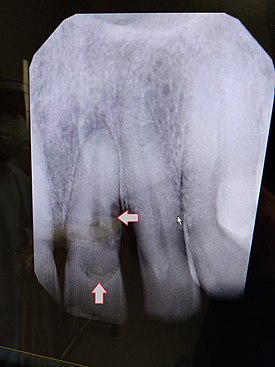
Tooth resorption
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Ihsan Maulana MustofaInformasi pribadiNama lahirIhsan Maulana MustofaKebangsaan IndonesiaLahir18 November 1995 (umur 28)Tasikmalaya, Jawa BaratTinggi174 cm (5 ft 8+1⁄2 in)Berat62 kg (137 pon) (137 pon)PeganganKananPasanganKulsum Nurul Jannah (m. 2018)Men's singlePeringkat tertinggi19 (4 Agustus 2016)Peringkat saat ini128 (3 Mei 2022) Rekam medali Mewakili Indonesia Kejuaraan Dunia Junior Bangkok 2013 Tunggal …

5,7 × 28 mm Peluru 5,7 × 28 mm untuk olahraga menembak. Dari kiri ke kanan: SS195LF, SS196SR, dan SS197SR. Tipe Personal defense weapon Negara asal Belgia Sejarah penggunaan Operasional 1991-present[1] Digunakan oleh P90 UsersFive-seven Users Perang Gulf War[1] Afghanistan War[2] Iraq War Mexican Drug War[3] Sejarah produksi Perancang Jean-Paul Denis (SS90)[4] Marc Neuforge (SS90)[4] Dirancang 1986-1990 (SS90)[1]…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada April 2016. Berkas:Behempas.jpgBehempas olahraga tradisional yang menggabungkan seni dan beladiri Behempas adalah olahraga tradisional Suku Dayak Tunjung dan Suku Dayak Benuaq, Kalimantan Timur.[1] Bahempas termasuk olahraga yang ekstrem dikarenakan menggabungk…

Sylvie KinigiKinigi pada 1993 Presiden BurundiPelaksana tugasMasa jabatan27 Oktober 1993 – 5 Februari 1994 PendahuluFrançois Ngeze (Pelaksana tugas)PenggantiCyprien NtaryamiraPerdana Menteri BurundiMasa jabatan10 Juli 1993 – 7 Februari 1994PresidenMelchior Ndadaye PendahuluAdrien SibomanaPenggantiAnatole Kanyenkiko Informasi pribadiLahir1953 (umur 70–71)Mugoyi, Provinsi Pedesaan Bujumbura, Ruanda-UrundiPartai politikUni Perjuangan NasionalAlma materUniversitas B…

Chek Lap Kok Hanzi tradisional: 赤鱲角 Hanzi sederhana: 赤𫚭角 Makna harfiah: Red Perch Cape Alih aksara Mandarin - Hanyu Pinyin: Chìliè Jiǎo Yue (Kantonis) - IPA: [tsʰɛ̄ːk làːp kɔ̄ːk] - Romanisasi Yale: chek laahp gok - Jyutping: cek3 laap6 gok3 Pulau Chek Lap Kok diwarnai merah pada peta ini Chek Lap Kok (Hanzi: 赤鱲角) adalah sebuah pulau di wilayah perairan di barat Hong Kong. Dengan luas 12.70 kilometer persegi, pulau ini merupakan pulau terbesar keempat di Hong Kong. …

Ini adalah nama Korea; marganya adalah Heo. Heo Young-jiHeo Youngji di fansigning Kara pada 30 Agustus 2014Nama asal허영지LahirHeo Young-ji30 Agustus 1994 (umur 29)Goyang, Gyeonggi, Korea SelatanNama lainHur Young-jiYoungjiPekerjaanPenyanyiaktrisentertainerKarier musikGenreK-popInstrumenVokalTahun aktif2014 (2014)–sekarangLabelDSP MediaArtis terkaitKaraChamsonyeoK.A.R.DDSP Friends Korean nameHangul허영지 Hanja許齡智 Alih AksaraHeo Yeong-jiMcCune–ReischauerHŏ Yŏ…

أبيدوس العرابة بالهيروغليفية محافظات مصر القديمة (كور)، ويرى موقع أبيدوس في الجنوب. أبيدوس (بالهيروغليفية: «أب-ب-دجو») مدينة بغرب البلينا سوهاج وقد كانت أحد المدن القديمة بمصر العليا. يجمع معظم علماء الآثار على أنها عاصمة مصر الأولى في نهاية عصر ما قبل الأسر والأسر الأربع الأ…

Disambiguazione – Geniere rimanda qui. Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Geniere (disambigua). Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento militari è priva o carente di note e riferimenti bibliografici puntuali. Sebbene vi siano una bibliografia e/o dei collegamenti esterni, manca la contestualizzazione delle fonti con note a piè di pagina o altri riferimenti precisi che indichino puntualmente la provenienza delle informazioni. Puoi migliorare questa voce citando le fonti più p…

RaiSat 1 - Cultura e spettacolo Paese Italia Data di lancio 27 ottobre 1997 Data chiusura 30 giugno 1999 Sostituito da RaiSat Art Editore RaiSat Diffusione Satellite Digitale in chiaro sul satellite Hotbird RaiSat 1 - Cultura e spettacolo è stato un canale televisivo satellitare gratuito dedicato alla cultura e allo spettacolo, edito da Rai e curato dalla sua direzione RaiSat. Storia e palinsesto Nasce nel 1997, insieme agli altri canali di RaiSat, all'epoca struttura della Rai che si occ…

Worldwide economic event Dow Jones Industrial Average Nasdaq Composite Index S&P 500 The 2022 stock market decline was an economic event involving a decline in stock markets globally. The decline was the worst for American stock indices since 2008, ending three-years of gains.[1] In February 2022, the Russian invasion of Ukraine caused a sell-off across many financial markets throughout the world. The stock market decline has had a serious negative impact on economies throughout the …

Indian cinematographer and film director PC Sreeram ISCBorn (1956-01-26) 26 January 1956 (age 68)[1]Madras, Madras State(now Chennai, Tamil Nadu), IndiaOther namesP. C, P. C. SriramAlma materMadras Film InstituteOccupation(s)Cinematographer, Film DirectorYears active1982–presentChildren2RelativesP. R. Sundaram Iyer (grandfather)[2]AwardsNational Film Award for Best Cinematography (1987) P. C. Sreeram ISC (born 26 January 1956) is an Indian cinematographer an…

Commune in Brașov, RomaniaMoieciuCommuneLocation in Brașov CountyMoieciuLocation in RomaniaCoordinates: 45°30′28″N 25°20′33″E / 45.50778°N 25.34250°E / 45.50778; 25.34250CountryRomaniaCountyBrașovGovernment • Mayor (2020–2024) Ioniță-Mircea Manea[1] (PNL)Area94.91 km2 (36.64 sq mi)Highest elevation1,200 m (3,900 ft)Lowest elevation800 m (2,600 ft)Population (2021-12-01)[2]…

BeataAnna KolesárováMartirLahir(1928-07-14)14 Juli 1928Vysoka nad Uhom, Distrik Michalovce, CekoslowakiaMeninggal22 November 1944(1944-11-22) (umur 16)Pavlovce nad Uhom, Košice, Republik SlowakiaDihormati diGereja Katolik RomaBeatifikasi1 September 2018, Stadion Lokomotíva, Košice, Slowakia oleh Kardinal Giovanni Angelo BecciuTempat ziarahPavlovce nad UhomPesta20 NovemberPelindungKaum mudaKorban pemerkosaanKorban pelecehan Beata Anna Kolesárová (14 Juli 1928 – 22 Nove…

Vicino alla fineEthan Hawke in una scena del filmTitolo originaleA Midnight Clear Paese di produzioneStati Uniti d'America Anno1992 Durata108 min Rapporto1,85:1 Genereguerra RegiaKeith Gordon SoggettoWilliam Wharton SceneggiaturaKeith Gordon ProduttoreMarc Abraham, Armyan Bernstein, Bill Borden, Margaret Hilliard, Dale Pollock, Tom Rosenberg FotografiaTom Richmond MontaggioDon Brochu Effetti specialiRick Josephsen MusicheMark Isham CostumiBarbara Tfank TruccoRyan Marie McCormick Interpreti e per…

Tour by the Indian Cricket Team in Sri Lanka during 2021 Indian cricket team in Sri Lanka in 2012 Sri Lanka IndiaDates 21 July – 7 AugustCaptains Mahela JayawardeneAngelo Mathews(5th ODI and Only T20I) MS DhoniOne Day International seriesResults India won the 5-match series 4–1Most runs Kumar Sangakkara (206) Virat Kohli (296)Most wickets Thisara Perera (8)Lasith Malinga (8) Irfan Pathan (8)Player of the series Virat Kohli (Ind)Twenty20 International seriesResults India won…

This article relies excessively on references to primary sources. Please improve this article by adding secondary or tertiary sources. Find sources: List of number-one urban albums of 2015 Australia – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) ARIA Chartsnumber-one urban albums of 2015< 20142016 >Other Australian number-one charts of 2015albumssinglesurban singlesdance singlesclub tra…

1924 film by Monta Bell The SnobLobby cardDirected byMonta BellWritten byMonta BellBased onThe Snob: The Story of a Marriageby Helen Reimensnyder MartinStarringJohn GilbertNorma ShearerConrad NagelCinematographyAndré BarlatierEdited byRalph LawsonDistributed byMetro-Goldwyn-MayerRelease date November 19, 1924 (1924-11-19) (United States) Running time70 minutesCountryUnited StatesLanguageSilent (English intertitles)Budget$100,000[1] The Snob is a 1924 American silent d…

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年5月6日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 约翰斯顿环礁Kalama Atoll 美國本土外小島嶼 Johnston Atoll 旗幟颂歌:《星條旗》The Star-Spangled Banner約翰斯頓環礁地�…

Ця стаття потребує додаткових посилань на джерела для поліпшення її перевірності. Будь ласка, допоможіть удосконалити цю статтю, додавши посилання на надійні (авторитетні) джерела. Зверніться на сторінку обговорення за поясненнями та допоможіть виправити недоліки. Матер…

此条目序言章节没有充分总结全文内容要点。 (2019年3月21日)请考虑扩充序言,清晰概述条目所有重點。请在条目的讨论页讨论此问题。 哈萨克斯坦總統哈薩克總統旗現任Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев卡瑟姆若马尔特·托卡耶夫自2019年3月20日在任任期7年首任努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫设立1990年4月24日(哈薩克蘇維埃社會主義共和國總統) 哈萨克斯坦 哈萨克斯坦政府與�…