Niyama
|

Indian military unit 27 AD Missile Regiment (Amritsar Airfield)Active1942 – presentCountryIndiaAllegiance British India IndiaBranch British Indian Army Indian ArmyTypeCorps of Army Air DefenceSizeRegimentMotto(s)“Sky high excellence”ColorsSky Blue and RedEquipmentAkash surface-to-air missiles[1]DecorationsVir Chakra 5Sena Medal 4Vishisht Seva Medal 2 Mention in Despatches 5Battle honours‘Amritsar Airfield’CommandersNotablecommandersLieutenant General Nav Kum…

Bulu setengah panjang asia Nama lain TiffanieBulu setengah panjang burmilla Asal Inggris Standar ras GCCF standar Kucing domestik (Felis catus) Kucing bulu setengah panjang asia (bahasa Inggris: Asian Semi-longhair cat; dikenal juga sebagai Tiffanie) adalah salah satu ras kucing yang hasil persilangan antara ras burma dengan ras persia chinchilla. Kucing bulu setengah panjang asia juga merupakan versi bulu sedang dari ras burmilla, sehingga sering disebut juga dengan kucing bulu seteng…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada November 2022. Ana MontesNama lahirAna Belén MontesKelahiran28 Februari 1957 (umur 67)Jerman BaratKebangsaanAmerika SerikatPekerjaanAnalis inteliejsni/Mata-mataAlma materUniversitas Virginia Universitas Johns Hopkins Ana Belén Montes[1] (lahir 28 Februar…

Ilustrados Ilustrado (Spanyol: terpelajarcode: es is deprecated ) adalah istilah yang digunakan untuk kaum terpelajar di Filipina selama masa kolonial Spanyol pada akhir abad ke-19. Mereka adalah masyarakat kelas menengah yang bersekolah menggunakan bahasa Spanyol dengan ide-ide liberalisme Spanyol serta nasionalis Eropa. Kelas ilustrado terdiri dari intelektual pribumi dengan campuran berbagai ras dan bahasa: Indios, Kreol (Insulares), dan Mestizos Filipino. Stanley Karnow, dalam karyanya In Ou…

This article consists almost entirely of a plot summary. Please help improve the article by adding more real-world context. (October 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Black Lightning is an American superhero television series developed by Salim Akil, airing on The CW. It is based on the DC Comics character of the same name, created by Tony Isabella. It stars Cress Williams as the titular character alongside China Anne McClain, Nafessa Williams, Christine Adams, Marvin Jo…

Group of stereoisomers AminoglutethimideClinical dataTrade namesElipten, Cytadren, Orimeten, numerous othersOther namesAG; AGI; Ba 16038; Ciba 16038; ND-1966; 2-(p-Aminophenyl)-2-ethylglutarimideAHFS/Drugs.comConsumer Drug InformationMedlinePlusa604039Pregnancycategory AU: D Routes ofadministrationBy mouthDrug classAromatase inhibitor; Antiestrogen; Steroidogenesis inhibitor; AntiglucocorticoidATC codeL02BG01 (WHO) Pharmacokinetic dataBioavailabilityRapid, complete[1]Metab…

Alyssa MilanoLahirAlyssa Jayne MilanoPekerjaanAktrisPenyanyiProduserTahun aktif1981–sekarangSuami/istriCinjun Tate (Januari-November 1999)Dave Bugliari (2009 - sekarang)AnakMilo Thomas Bugliari (2011)Elizabella Dylan Bugliari (2014)Situs webhttp://www.alyssa.com/ Alyssa Jayne Milano (lahir 19 Desember 1972) adalah seorang aktris berkebangsaan Amerika Serikat. Dia menjadi terkenal saat diperankan sebagai Samantha Micelli di Who's the Boss?. Dilahirkan di Brooklyn, New York. Ia memulai kari…

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Desember 2022. Viktor RydbergRydberg in 1876LahirAbraham Victor Rydberg(1828-12-18)18 Desember 1828Jönköping, SwedenMeninggal21 September 1895(1895-09-21) (umur 66)Djursholm Abraham Viktor Rydberg ( Jönköping, 18 Desember 1828 - Djursholm, 21 September 1895) a…

Ini adalah daftar katedral di Papua Nugini diurutkan berdasarkan denominasi. Katedral Santa Maria, Port Moresby Katolik Katedral Gereja Katolik di Papua Nugini:[1][2] Katedral Santo Ignasius, Aitape Katedral Hati Kudus Yesus, Alotau Katedral Bunda Maria dari Hati Kudus, Bereina Katedral Bunda Maria Dikandung Tanpa Noda, Hahela Katedral Santo Gerardus, Kiunga Kon-Katedral Santo Louis de Montfort, Daru Katedral Maria Penolong Umat Kristiani di Kefamo, Goroka Katedral Bunda Maria da…

Sweden is home to thirteen species of amphibians and six species of reptiles. All nineteen species are protected throughout the country. Amphibians Scientific name Common nameSwedish name Description Image Notes Bombina bombina European fire-bellied toadKlockgroda Bufo bufo Common toadVanlig padda Adults are about 15 centimetres (6 in) long and colored brown, olive-brown or greyish brown. Bufo viridis European green toadGrönfläckig padda Epidalea calamita Natterjack toadStrandpadda/Stinkp…

Carukiidae Malo kingi Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Cnidaria Kelas: Cubozoa Ordo: Carybdeida Famili: Carukiidae Genus Carukia Southcott, 1967 Gerongia Gershwin & Alderslade, 2005 Malo Gershwin, 2005 Manokia Southcott, 1967 Morbakka Gershwin, 2008 Carukiidae adalah famili ubur-ubur kotak dalam kelas Cubozoa.[1] Spesies Carukia Berisi spesies berikut: Carukia barnesi Southcott, 1967 Carukia shinju Gershwin, 2005 Gerongia Berisi spesies berikut: Gerongia rifkinae Gershwin…

Versi berduri dari gedik tikam petani bergagang panjang. Dari manual tempur Paulus Hector Mair Arte De Athletica Gedik tikam adalah senjata yang terdiri dari kepala pemukul yang diikatkan pada pegangan dengan tali, atau rantai yang fleksibel. Keutamaan taktis utama dari pukulan ini adalah kemampuannya untuk menyerang perisai atau tangkisan pemain bertahan. Tanggung jawab utamanya adalah kurangnya presisi dan kesulitan menggunakannya dalam pertempuran jarak dekat, atau formasi jarak dekat. Ada du…

Katedral StamfordKatedral Santo VladimirInggris: St. Vladimir's Cathedralcode: en is deprecated Katedral Stamford41°03′41.93″N 73°31′39.82″W / 41.0616472°N 73.5277278°W / 41.0616472; -73.5277278Koordinat: 41°03′41.93″N 73°31′39.82″W / 41.0616472°N 73.5277278°W / 41.0616472; -73.5277278Lokasi24 Wenzel TerraceStamford, ConnecticutNegaraAmerika SerikatDenominasiGereja Katolik Roma(sui iuris: Gereja Katolik Yunani Ukraina)Arsite…
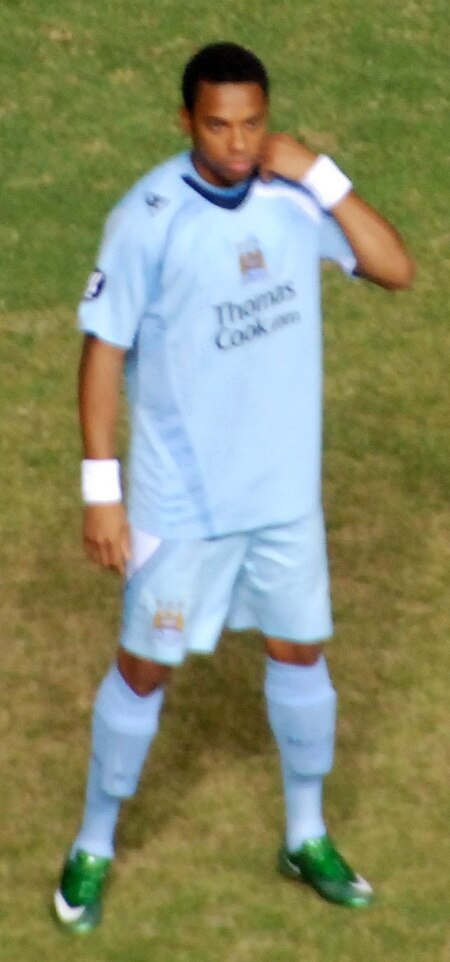

Robinho Robinho entrenando con el MilanDatos personalesNombre completo Robson de SouzaApodo(s) RobinhoNacimiento São Vicente, Brasil25 de enero de 1984 (40 años)Nacionalidad(es) BrasileñaCarrera deportivaDeporte FútbolClub profesionalDebut deportivo 2002(Santos F. C.)Posición DelanteroDorsal(es) 7,10,56,70Goles en clubes 249Retirada deportiva 2020(Santos F. C.)Selección nacionalSelección BRA BrasilDebut 13 de junio de 2003Dorsal(es) 7,10,11,18,23Part. (goles) 100 …

Polygamy was outlawed in federal territories by the Edmunds Act, and there are laws against the practice in all 50 states, as well as the District of Columbia, Guam,[1] and Puerto Rico.[2] Because state laws exist, polygamy is not actively prosecuted at the federal level.[3] Many US courts (e.g. Turner v. S., 212 Miss. 590, 55 So.2d 228) treat bigamy as a strict liability crime: in some jurisdictions, a person can be convicted of a felony even if he reasonably believed he…

Cyclostomi Periode Lochkovium - Masa kini 419.2–0 jtyl PreЄ Є O S D C P T J K Pg N Cyclostomata Perik laut dari SwediaTaksonomiKerajaanAnimaliaFilumChordataSuperkelasCyclostomata Duméril, 1806 Kelas Myxini (Belut lintah) Hyperoartia (perik) lbs Cyclostomi, terkadang dirujuk sebagai Cyclostomata /sɪkloʊˈstɒmətə/, adalah sebuah kelompok hewan vertebrata yang mencakup ikan tak berahang yang masih hidup: lamprey (perik) dan ikan hag (belut lintah). Kedua kelompok memiliki mulut tak b…

International goals by Cristiano Ronaldo Ronaldo celebrates after scoring a penalty against New Zealand at the 2017 FIFA Confederations Cup in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Cristiano Ronaldo is a Portuguese professional footballer who has represented the Portugal national team since his debut on 20 August 2003 against Kazakhstan in a friendly.[1] He would later score his first international goal on 12 June 2004, during a UEFA Euro 2004 group stage match against Greece.[2] Since then,…
Gua Lubang VCMLeang Lubang VCMLokasiKabupaten Maros, Sulawesi Selatan, IndonesiaKedalaman220 mGeologikarst / batu kapur / batu gampingSitus webvisit.maroskab.go.idcagarbudaya.kemdikbud.go.id Gua Lubang VCM atau Leang Lubang VCM (Inggris: VCM Hole Cave ) adalah sebuah gua di Kawasan Karst Maros-Pangkep, Taman Nasional Bantimurung-Bulusaraung, wilayah administratif Kabupaten Maros, Sulawesi Selatan, Indonesia. Gua ini adalah jenis gua alam dan gua vertikal dengan kedalaman 220 meter. Secara m…

Northrop F-5F-5E/F Tiger II milik TNI AU.TipePesawat tempur serangPerancangEdgar SchmuedTerbang perdana30 Juli 1960 (F-5A)11 Agustus 1972 (F-5E)StatusDipensiunkan sejak 3 Mei 2016Pengguna utamaAmerika SerikatPengguna lainIndonesiaBrasil35 negara lainJumlah produksi836 A/B/C1400+ E/FHarga satuanUS$2,1 juta (Rp32,51 Miliar) (F-5E)[1]Acuan dasarT-38 TalonVarianCanadair CF-5 F-20 Tigershark Berkas:IAF 0214.jpgPesawat Hawk 200 dan F 5 dari TNI AU Berkas:Photo 2005523 135039.jpgPesawat F-5t me…

Ilustrasi dari Types of Mankind (1854), penulisnya, Josiah Clark Nott dan George Robins Gliddon berpendapat bahwa bangsa Negro berada pada peringkat penciptaan antara bangsa Yunani dan simpanse. Artikel ini adalah bagian dari seri tentangPengobatan alternatif dan semu Informasi umum Pengobatan alternatif Perdukunan Sejarah Kebangkitan pengobatan modern Ilmu semu Pengobatan semu Antisains Skeptisisme Gerakan skeptis Nihilisme terapeutik Kedokteran dan sains pinggiran Akupunktur Akupresur Air…


